Download the conference program (short | with abstracts)
Download the presentation schedule (xlsx)
Full papers are available here until they are posted on ASEE’s website (sometime after the conference). Refer to the paper ID below.
Presentations have an attached code in the form “A.1.2 indicating the room, session and time slot respectively.
Instructions for Session Chairs
Contents
- 1 Timeslots & Topics
- 2 Presenters & Abstracts
- 2.1 Meredith Lauren Sander
- 2.2 Raul Armendariz
- 2.3 Erick Martinez
- 2.4 Vazgen Shekoyan
- 2.5 Kelly Miller
- 2.6 Mohsen Mosleh
- 2.7 Wyatt John Ritchie
- 2.8 Vanessa L Eyer
- 2.9 Brian Maicke
- 2.10 Tak Cheung
- 2.11 Erin A Hostetler
- 2.12 Liyong Sun
- 2.13 Samantha Deokinanan
- 2.14 Asad Azemi
- 2.15 Michael S. Lehman
- 2.16 Peter Raymond Stupak
- 2.17 Adekola Owolabi
- 2.18 Marietta Scanlon
- 2.19 Peter Raymond Stupak
- 2.20 Thuong N Nguyen
- 2.21 Te-Shun Chou
- 2.22 Akin Tatoglu
- 2.23 Dugwon Seo
- 2.24 Kala Meah
- 2.25 Brad Sottile
- 2.26 Asad Azemi
- 2.27 Yue Hung
- 2.28 Tak Cheung
- 2.29 Kimberly Riegel
- 2.30 Abdullah Konak
- 2.31 Steven Barton
- 2.32 Rajarajan Subramanian
- 2.33 Emily Alexandra German
- 2.34 Ryan Scott Hassler
- 2.35 Robert L. Avanzato
- 2.36 Erin A Hostetler
- 2.37 Joseph Michael Mahoney
- 2.38 Christian Enmanuel Lopez
- 2.39 Ge Jin
- 2.40 Matthew Rhudy
- 2.41 Matthew Jason Bilsky
- 2.42 Alex C. Szatmary
- 2.43 Ashwin Satyanarayana
- 2.44 Michael Lawrence
- 2.45 Jason Lehrer
- 2.46 James J. Scire
- 2.47 Yong Zhu
- 2.48 Ivan E. Esparragoza
- 2.49 Christine Masters
- 2.50 Shane Rogers
- 2.51 Jason Jiang
- 2.52 Michael R. Bartolacci
- 2.53 Dorothy Carter
- 2.54 Nicholas Patrick Haring
- 2.55 Baha Bachnak
- 2.56 Chris R Fatzinger
- 2.57 Cory David Jamieson
- 2.58 Jesse Wengel
- 2.59 Sachin P Patil
- 2.60 Ryan Blankenbiller
- 2.61 Angela Davis
- 2.62 Gabriela Gonzalez-Magana
- 2.63 Mpila Makiesse Nkiawete
- 2.64 Caedmon DelVecchio
- 2.65 Thomas Jones
Timeslots & Topics
Session 1
Posters
Session 2
Session 3
Session 4
Presenters & Abstracts
Meredith Lauren Sander
A.1.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Behrend
Analysis of Electrically Conductive Polymer Composites as Bipolar Plates – 20996
The effectiveness of a microscale direct methanol fuel cell is largely dependent on the ability of its bipolar plates to conduct electricity. Traditionally, metal alloys are used as current collectors due to their inherent high electrical conductivity properties. However, polymer composites offer a promising alternative to metal alloys as they are lightweight, cheaper, and easier to produce if using an injection molding process. Current research has mostly tried using only one filler to attempt to achieve conductivity levels needed for a fuel cell application. In this study, different conductive fillers were compounded into nylon 6,6 plastic at various weight percent in order to determine the optimum filler-to-polymer ratio for electrical conductivity. The fillers most applicable to this research are a blend of carbon fiber and carbon black. From this research, it was found that carbon fibers at a high weight percent provided samples with the highest conductivity. This was true only when samples were not compounded prior to injection molding. It was also seen that adding carbon black into the process did not improve conductivity. Hopefully more research into electrically conductive polymers will reduce the cost of fuel cells so that they can be implemented into our everyday life.
Raul Armendariz
A.1.2
Queensborough Community College
Design and construction of a cosmic ray detector array for undergraduate research at the City University of New York – 21006
Cosmic ray detectors are being built by undergraduate engineering and computer science research students, high school teachers, and college faculty, for a detector array at campuses of the City University of New York. One hundred surplus plastic scintillators were donated from the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, and 100 decommissioned photomultiplier tubes obtained from the Brookhaven National Laboratory for the detectors. This paper discusses the quality testing of photomultiplier tubes and the scintillator, the detector design, and cosmic ray measurements using the QuarkNet data acquisition board. Students are involved over the course of their undergraduate studies via research and scientific computing courses, and REU summer internships at the national laboratories. By involving students, teachers, faculty, and research scientists from eight different institutions a learning community has been established.
Erick Martinez
A.1.3
United States Military Academy
An Environmental Engineering Sequence: Deliberately Addressing and Evaluating Environmental Attitudes and Knowledge – 21035
The need for improved environmental knowledge and attitudes has never been greater due to increased stress on Earth’s resources. The unique pedagogical structure of an engineering sequence at the undergraduate level provides a means to improve environmental knowledge and attitudes. This increase in skill sets enables permeation of sound science and principles that have the potential to influence policies made by the next generation of leaders. This study explored the environmental knowledge and attitudes of two different populations including those with a STEM and non-STEM academic field of study taking a similar introductory environmental science course at the United States Military Academy. Initial environmental knowledge differences between Hispanic/Latino and Black/African American students (p=0.0137), between Black/African American and White students (p=0.0002), and between male and female students (p=0.0016) were found to be statistically significant. After taking an environmental science course at the undergraduate level, our results suggest that these differences are no longer significant.
Vazgen Shekoyan
A.1.4
CUNY Queensborough Community College
Latent variable modeling with applications to education assessment and NSF-REU projects for engineering students – 21023
The latent variable modeling technique in education assessment is illustrated using problem solving examples in first semester physics for engineering and technology students. The regression modeling of data in the Newton second law laboratory class has equivalence to an analysis with the internal force serving as the latent variable. A path diagram would contain the internal force as a latent variable which manifest its influence on the observed datasets, namely, acceleration and force. Similarly, the pre-score and post-score data collected for education assessment can be studied with latent variable modeling to broaden the scope beyond regression which requires an independent variable. The numerical and flexibility advantages of latent variable modeling versus regression modeling in education assessment are presented. Free LISREL student version working details and free confirmatory factor analysis Microsoft Excel software from university faculty are presented. The adaptation of Queensborough Community College Physics faculty education research into Queensborough NSF-REU projects for engineering students is discussed.
Kelly Miller
A.2.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Behrend
Burst Testing of Biomaterials for Medical Applications – 20988
The process of creating novel, 3D-printed hernia meshes will optimize the way current traditional meshes are produced and will facilitate the custom-design and functionalization of surgical meshes. 3D-printed hernia meshes based on new biodegradable citrate-polymers have been developed in our lab. Preliminary burst strength tests for the 3D-printed meshes must be executed to ensure a tear will not occur once implanted. In this work, an apparatus was designed and machined in accordance with ASTM Standard D6797 Ball Burst Test and attached to an Instron 5966 testing machine to collect data. Materials burst strength tests were conducted on polycaprolactone, poly (1, 8-octanediol citrate), chitosan film, and aluminum foil as a control to validate the device although it was found that 3D-printed hernia meshes provide lower burst strengths than that of the abdominal wall.
Mohsen Mosleh
A.2.2
Howard University
Design, Build, and Test Projects in an Engineering Materials Laboratory – 20974
A design, build, and test (DBT) approach for studying the mechanical behavior of materials in an engineering materials laboratory is shown to create a flexible learning environment which imparts thinking competencies. Traditionally, students have utilized conventional testers such as a universal testing machine for studying the stress-strain relationship and for measuring properties such as the modulus of elasticity and shear modulus. In the DBT approach, the student teams designed and built single-task devices and tested them for measuring specific mechanical properties. The surveys affirmed that student engagement, self-reliance, problem solving, and teamwork which are attributes of the project-based learning (PBL) method were improved. Additionally, innovative thinking in face of cost constraints and gaining manufacturing and assembly skills were enhanced because of the design and build activates. As the student teams advanced through the projects in the laboratory, the accuracy of measured properties compared with the nominal values notably increased.
Wyatt John Ritchie
A.2.3
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
The Creation of an Immersive Environment to Provide Shop Equipment Training – 21013
The purpose of this project was to create an immersive environment to provide an introduction to machine shop equipment on the Penn State Berks campus. Using a 360o video camera, operational videos of a lathe, vertical band saw, horizontal band saw, mill, and arc welder were produced. The videos were edited to incorporate informational narration and processed for viewing on either a desktop computer, or with an immersive virtual reality (VR) headset. Videos were published and distributed such that the instructional videos could easily be incorporated into a curriculum. Results of the project will be assessed for both immersiveness as well as pedagogical value.
Vanessa L Eyer
A.2.4
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
Stimulating the Senses: Career Development for Students and How the Library Can Help – 21052
The poster will focus on the following topics: The Development of two collection in Penn State UP Engineering Library: Professional development collection – books and ebooks on choosing your career, FE Exam prep, developing presentation, technical writing and interview skills, and diversity in engineering. We have also partnered with the UP College of Engineering’s Career Resources & Employer Relations department to add titles to the collection. Popular technology collection – books and ebooks focusing on historical events and figures, current trends, developments and hot topics related to engineering. Books are more relaxed in nature to remind students why they love engineering and to stimulate their interests. Adding career development sections to libguides. Partnering with faculty to develop an assignment for freshman seminars and GenEd courses that focuses on career development. Freshman struggle with understanding how the use of databases and scholarly resources is helpful. Many freshman are also trying to decide what major they want to study, field of engineering they want to go into and how to find an internship. Faculty are looking for assignments that could be worth 1-3 credits. A short assignment that introduces scholarly resources in a way that students can relate to may help them appreciate the use of scholarly resources for future projects and in the professional world.
Brian Maicke
A.3.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Harrisburg
Undergraduate Propulsion Research at Penn State Harrisburg – 21012
This paper describes current efforts Penn State Harrisburg, an undergraduate college and graduate school of The Pennsylvania State University, to involve undergraduate students in aerospace propulsion research. A summary of past and present research projects with undergraduate student participation is provided. These projects range from the simulation of a propulsion subsystem, a rocket nozzle or helicopter rotor for example, to the design and fabrication of a functioning rocket engine. An examination of individual and group research work conducted through a range of activities including funded research, independent study, and capstone projects is presented. Examples of student successes include presentations at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) Region I Student Conference and the AIAA Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, journal publications in the AIAA Journal and Aerospace Science and Technology, and graduate fellowships through Department of Defense SMART Scholarship for Service Program. The paper concludes with strategies for student success as well as discussion of lessons learned during the past five years of propulsion research.
Tak Cheung
A.3.2
CUNY Queensborough Community College
Extraction of information and facts from data mining of random sequences for undergraduate research – 20998
A general method to extract information and facts from data mining of random sequences in biology and astronomy has been developed. The random sequence analysis has been implemented in several NSF-REU projects using NIH and NASA databases. Examples of RNA sequence with reference to Shannon-entropy based bioinformatics and SDO magnetic topology analysis with reference to solar physics are presented. The contrast to Brookhaven Synchrotron and high energy physics data analysis is also discussed. The feedback of administrating REU projects to our physics teaching for engineering students was found to be valuable and the examples of magnetic reconnection and geomagnetic induced current are presented. Therefore community college REU project provides connectedness awareness in the linking of previous published reports, critical thinking in result interpretation, and career development when going onto a senior college REU program, the top three benefits of college education, according to a 2016 July Money Magazine ”Value of College” survey.
Erin A Hostetler
A.3.3
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
Preparing First Year Engineering Students for Success through Research Exposure – 21008
How do you get a first year student to consider becoming involved in research? Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) programs have an incredible impact on the students who participate. The experience empowers students to better conceptualize course material in the classroom, determine areas of interest, and explore career paths. Studies show REU participants have higher grades and a higher likelihood of attending graduate school. Moreover, the earlier an undergraduate becomes involved in research, the larger impact the REU has on their overall success and retention in their chosen fields. ENGR 097 is a one-credit seminar taught at The Pennsylvania State University, University Park campus, focused on preparing first-year students to succeed in engineering through the lens of research. As a result, students learn more about engineering research and majors, develop success skills including time management and goal setting, and become familiar with resources. Faculty are connected to research minded students through course assignments and visible to students through a different lens. The REU seminar course is easily adaptable and can lead to an increase of engineering students in the pipeline for graduate studies.
Liyong Sun
A.3.4
The Pennsylvania State University, Erie
Preliminary Measurement of Through-plane Thermal Conductivity and Contact Resistance – 20985
Thermal conductivity and contact resistance in fuel cell materials are critical to the temperature distribution in fuel cell. A Research Experience for Undergraduate project, which will expand the ability of current test setup in the thermal lab to measure the thermal conductivity and contact resistance of the graphite, is introduced. The experiment results is presented and discussed.
Samantha Deokinanan
A.3.5
City College of the City University of New York
International Research Training: Investigating Public Transportation Commuting in Feira de Santana (Bahia), Brazil. – 21057
Integrating an International Experience in Undergraduate Education is increasingly seen as an important component of high impact undergraduate activities. These usually take the form of student exchanges, internships, service learning experiences and short-term faculty led study abroad programs. An International Summer Research focused on Transportation was developed utilizing the design and distribution of a Comprehensive Transportation Survey (CTS) in Feira de Santana, Bahia state (Brazil). In collaboration with the State University of Feira de Santana, the CTS was developed in Summer 2016 by a team of three Louis Stokes Alliance scholars. A team of ten students at State University of Feira de Santana were trained and engaged in conducting the surveys at six bus terminals in Feira de Santana in Fall 2016 for initial data collection. A more extensive CTS for online deployment was also developed and was launched in Summer 2017. Surveys collected were analyzed to determine general bus utilization demographics, origin-destination, transportation mode, time of travel, transportation costs, travel satisfaction, and significant flows. The results on the level of satisfaction have a significant influence on the probability of choosing a bus for trips. It was found that, in some cases, travelers continue to use the bus services even if their levels of satisfaction with some service attributes are low because they lack options for their trips. The results obtained can be augmented and utilized to address the increased ridership projected for Feira de Santana as the population is projected to increase to one million by the year 2040.
Asad Azemi
A.4.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Brandywine
Promoting Innovation and Entrepreneurship as part of Curriculum – 21011
Promoting entrepreneurship is not a new concept in academia. It is a concept that has been embraced by large and small universities. Entrepreneurship is promoted through several means that include dedicated centers, courses, academic minors, and activities and events. In regard to innovation, we can identify two major issues. First, innovation, due to its nature, does not enjoy the same kind of promotion and resource allocation by universities. Second, many universities use innovation in conjunction with entrepreneurship as a natural add-on and then focus on promoting entrepreneurship. This is understandable since it may be difficult to come up with a consensus on how to teach innovation as part of the curriculum. In this regard, we need to answer the difficult questions about the nature of innovation, hereditary or not, and if it can be learned/taught. Like many others, we also believe that innovation cannot be taught but it can be enhanced for those who have the required natural abilities. We believe that this can be accomplished by teaching systems thinking and design methodology, which can be part of the curriculum. Furthermore, such an addition will also benefit the general student population by introducing them to the aforementioned subjects, which are quickly becoming required skills in today’s world. The focus of the paper is to present systems thinking and design methodology and courses that need to be added to the curriculum, as a to promote innovation and entrepreneurship, so that all students are exposed and benefit from these subjects.
Michael S. Lehman
A.4.2
Lehigh University
Intellectual Potpourri: Teaching Emerging Entrepreneurs Intellectual Property – 20991
‘What does it mean when my patent application publishes?’ ‘How do I find if my idea for a product name is trademarked?’ ‘What are the key negotiating points of a licensing deal?’ ‘How do I effectively use trade secrets in my business strategy?’ These are questions early stage innovators grapple with as they navigate the world of intellectual property. The Master’s of Engineering in Technical Entrepreneurship at Lehigh University has implemented a curriculum that arms its graduates with knowledge and skills related to intellectual property. From day one of the twelve-month program, students are introduced to patents, trademarks, copyrights and trade secrets (Bloom’s Taxonomy level 1-Knowledge). Live case studies with engineering entrepreneurs provide opportunities to extrapolate how IP can be used strategically in the venture (Bloom’s level 2-Comprehension). Student then delve into the specifics of patents, trademarks, university tech transfer and licensing opportunities as related to an industry of interest (Bloom’s level 3-Application). They also use their knowledge of IP to aid in application of creativity and innovation techniques. In the next semester, students continue to apply intellectual property concepts in theory courses related to integrated product development and entrepreneurship (Bloom’s levels 3-Application and 4-Analysis). A week-long intensive immersion with technologies developed at Lehigh and protected via patents through the Office of Technology Transfer offers additional reinforcement of learning. During the final set of project classes, students have the opportunity to create and protect their own intellectual property as related to their personal venture (Bloom’s levels 5-Synthesis and 6-Evaluation). Graduates of the program have been had patents issued and are selling goods and services under federally-registered trademarks.
Peter Raymond Stupak
A.4.3
Raritan Valley Community College
IllumiNUT Shake-Light Manufacturing: An Engineering/Business Interdisciplinary Supply Chain Project – 20983
An innovative inter-disciplinary project was launched at Raritan Valley Community College (RVCC) in Fall 2016 where Engineering and Business students participate hands-on in the operation of a supply-chain manufacturing business. The product, the “IllumiNUT”, is a customized green-energy shake-light that provides battery-free light just by shaking it. Originally developed by a group of four RVCC Engineering students in Fall 2015, the IllumiNUT product was a result of the RVCC “Authentic Engineering Experience” course where students are tasked with designing and developing a real product for a real customer. The Engineering-Business collaboration began in Spring 2016 when the RVCC chapter of the international student-business organization, Enactus, saw the potential in the IllumiNUT as an entrepreneurial venture. Made entirely by students on-site at the RVCC campus, no part of the IllumiNUT manufacturing is outsourced. Manufacturing emphasis is on product quality and process improvement using Lean Manufacturing methods to elimination of waste. Sales are done personally and face-to-face to directly learn the customer needs and to build the IlluminNUT brand at the same time. All manufacturing and business metrics are tracked to follow the health of the business. Leadership and participation for each part of the IllumiNUT “business” is provided by students. Engineering and Business students literally work side by side breaking down traditional and persistent interdisciplinary communications barriers. A total of 78 student-made IllumiNUT products were sold as of April 2017, generating just over $1000 in revenue. The IllumiNUT profit was donated to a Local Food bank to demonstrate the positive impact of business on the community.
Adekola Owolabi
A.4.4
Centre for Entrepreneurial Research and Development Subsidiary of David Richard Associates
Bootstrapping Strategies for Launching Engineering Start Ups – 21003
Most people in STEM fields are quick to conclude that they are not cut out for business. This notion is very common among Medical Practitioners. Engineers are no exception either. The average engineer will rather play safe by opting for the comfort of a paid job. What most people don’t know is that entrepreneurship is not an easy game and to win in this game the prospective entrepreneur must be prepared to play the game by the rules. One very important rule is that the prospective entrepreneur must be ready to manage the attendant risks of starting a new business. One major risk is the total loss of the seed capital employed in launching the business and the best way to manage this risk is to reduce the seed capital that will be employed to the barest minimum. Another word for the act of minimizing resources used in starting a business is Bootstrapping. This paper examines Bootstrapping strategies that can be easily employed by engineering firms particularly the ones being launched by those new to entrepreneurship.
Marietta Scanlon
B.1.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
FiERCE: Empowering Girls in Engineering Through Role-Models and Mentoring – 21002
Leveraging current research indicating that the presence of mentors and role-models are instrumental to the recruitment and retention of females in engineering, the primary purpose of this study was to examine the effect of role-models and mentors on the attitudes and self-confidence of middle school girls towards engineering. Participants were cohorts of middle school aged females, paired with Penn State University female undergraduate engineering students. The study was conducted by exposing participants to a consistent series of activities that fostered creative thinking, problem-solving, and real-world engineering, all while encouraging and facilitating interaction among the cohorts. Comprehensive assessments were embedded into every aspect of the program in order to evaluate program effectiveness and outcomes. Regular, structured interactions between the participants resulted in statistically significant increases in both interest and confidence in engineering as well as the positive influence of mentors and role-models.
Peter Raymond Stupak
B.1.2
Raritan Valley Community College
Green Energy Tent-Light with GPS Locator: A Real Product for a Real Customer – 20984
In late January of the Spring 2017 semester, a Raritan Valley Community College (RVCC) Authentic Engineering Experience Team of three engineering and one computer science student sophomores received a request from a Customer, an avid backpacker, for a tent light which provides readable light for two people for thirty minutes without the use of batteries. In addition, the tent light would also function as a GPS receiver/Cell transmitter sending location coordinates to a phone or web-site at the Customer’s home. Other constraints, such as weight, dimensions, and water resistance were defined, but the Customer did not indicate or suggest how to achieve the required product performance – those decisions were left entirely to the student Team. The Customer required a finished product by the delivery date of May 1, 2017. The student Team members were treated as Professional Engineers in an Engineering-Solutions company – not as students. Although guided by industry-experienced staff, the overwhelming emphasis was for the student Teams to reach their own designs, experience their own failures and successes, resolve their own communications conflicts, and respond to critical Customer comments. The objective is for students to be exposed early in their academic careers and under “authentic engineering” conditions, to vital skills and practices used daily by professional Engineers. Most importantly students are taught – and experience first-hand – that success comes from never giving up. These experiences differentiate students and gives them an authentic story to relate to potential internship and professional employers.
Thuong N Nguyen
B.1.3
York College of Pennsylvania
Capstone Project: A Cloud-based Backend Server for an Automated Bicycle Rental System – 20975
Automated bicycle rental systems have become an increasingly popular form of public transportation in cities and on campuses. As a senior capstone project at York College of Pennsylvania, 19 engineering students across three disciplines; computer engineering, electrical engineering, and mechanical engineering; designed and built a working Automated Bicycle Rental System (ABRS) for use by the college community. The ABRS project is designed to support multiple rental kiosks, and a multitude of bicycles, each with an embedded GPS tracking device. Each rental kiosks and GPS tracking device communicates with a common backend server to provide status updates on system health, bicycle availability, as well as rental transaction information. The backend server maintains this information and provides both an end user and administrative user interface for interacting with the system. This paper presents the design and implementation of the cloud-based backend server for the ABRS project.
Te-Shun Chou
B.1.4
East Carolina University
Enhancing Students’ Hands-On Skills of Wireless Technology Using Network Simulators – 20978
This paper describes two well-known network simulators: Packet Tracer and Riverbed Modeler, and their core functionalities in the modeling of wireless networks. Labs were designed to aid students’ in learning wireless communication technologies. We expected the labs to help students gain practical experience working with wireless networking configurations and enhance their understanding of different wireless network topologies. At the end of the semester, a survey was conducted to evaluate the learning environment, simulators, and labs’ effectiveness. The results showed that most of the respondents had a very positive attitude toward the lab exercises. They also agreed that the simulators have successfully helped them develop their capabilities in creating and analyzing wireless networks in real world scenarios.
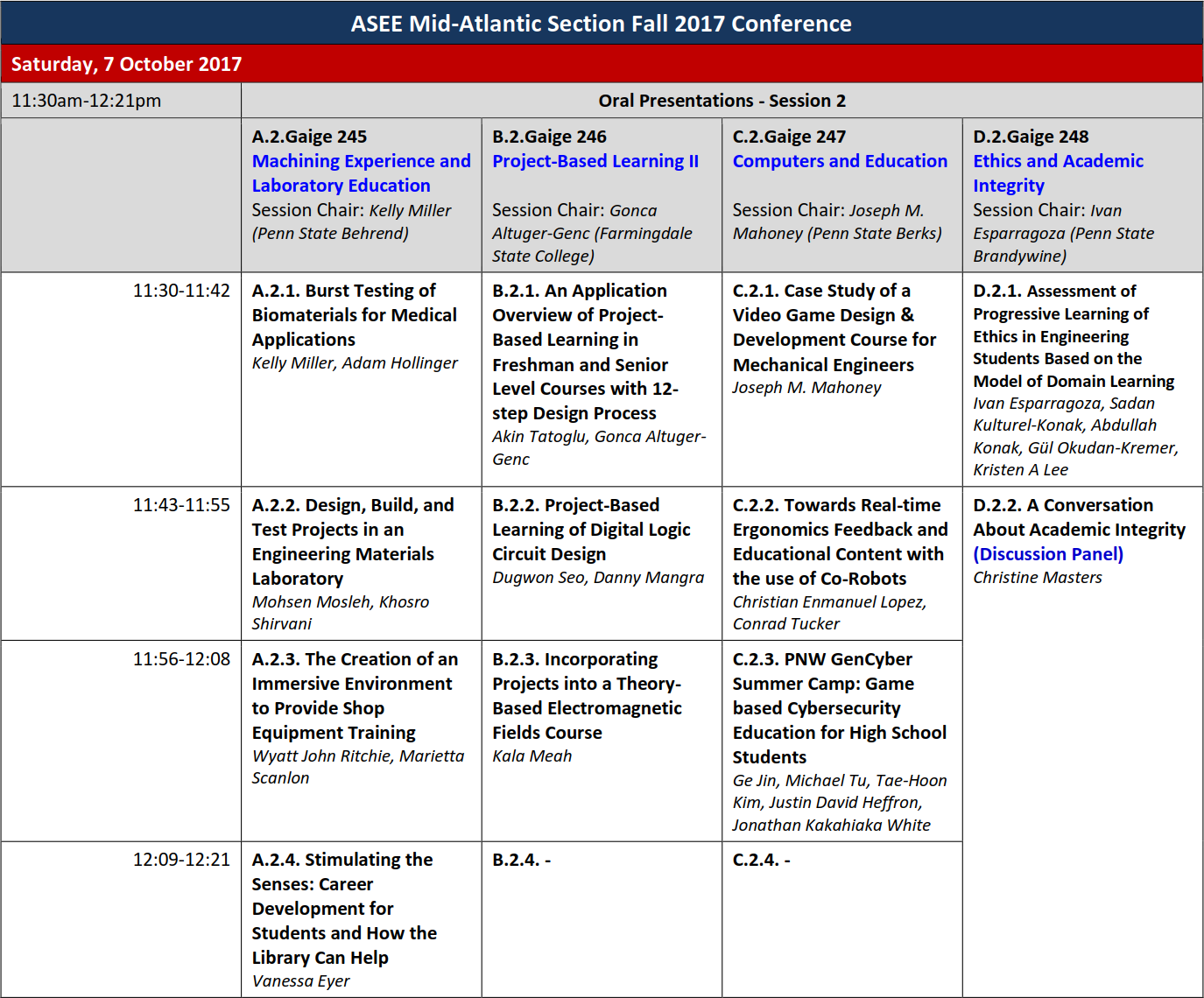
Akin Tatoglu
B.2.1
University of Hartford
An Application Overview of Project-Based Learning in Freshman and Senior Level Courses – 21020
Project based learning is an effective pedagogical strategy that can be implemented to various engineering courses from freshman to senior level. Flexible nature of the project-based learning allows instructors to custom design their projects to complement their courses’ learning objectives while providing a more effective learning environment for students to practice mathematical tools and skills. Project-based learning approach may have different goals and expectations for freshman students than senior students. In this paper, we review two project-based learning approaches following 12-step design process for freshman level mechanical engineering technology course and senior level mechanical engineering course. Design steps, implementation and timeline of assigned tasks, expected deliverables, and assessment of the projects will be discussed. Finally, execution of 12-step design process with a timeline is presented and discussed.
Dugwon Seo
B.2.2
Queensborough Community College
Project-Based Learning of Digital Logic Circuit Design – 21047
Digital Logic Design is a fundamental course in both Computer and Electrical Engineering Technology fields and as such it is important for the course to provide students a good understanding and continuous interest. Project-based learning allows students to gain knowledge and skills by solving real-world problems and helps to develop critical thinking, teamwork and self-management skills. In this paper, a description of the effective and innovative logic circuit design project is presented. This project can be used in class with first year community college students in Electrical and Computer Engineering Technology fields. The objective is to design a logic circuit to control a motorized device that moves by a signal from photocell sensors. The project exercises using Boolean logic functions, conducting a truth table, and assembling the logic gates to design the circuit that transmits the signals between photocell sensors and two motors. This covers the theoretical parts of the digital logic system. In addition to digital electronics understanding, the project delivers interdisciplinary features that bring knowledge of mechanics, circuit analysis, and 3-D printer use to the students. Through the practice of the student-driven project-based learning method, the students are expected to succeed in their transitions to higher-degree education and in their future STEM careers.
Kala Meah
B.2.3
York College of Pennsylvania
Incorporating Projects into a Theory-Based Electromagnetic Fields Course – 20976
Electromagnetic Fields at York College of Pennsylvania was designed to provide students with theoretical backgrounds on Maxwell’s equations and their applications to engineering problems. Topics include electrostatics, magnetostatics, magnetic fields and matter, induction, and electromagnetics waves. Students’ feedback from the initial offereings of this course indicated that students would like to have hands-on activities to apply the theories they were learning in the class. Students also pointed out that this course looked like another mathematics course without any hands-on activities. To facilitate hands-on experiences in the course, the instructor added two small-scale team projects: one on electrostatics and another on magnetostatics. This paper discusses the method of incorporating projects into a theory-based electromagnatic fields course as well as students’ feedback regarding project expereicnes and the overall course. This paper also includes brief descriptions of student projects along with testing and fabrication results.
Brad Sottile
B.3.1
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
Scaling for the Future: Development of a Sustainable Model for Teaching MATLAB Programming to STEM Students – 21029
An undergraduate programming language course in MATLAB has experienced explosive enrollment growth over the last decade at the Pennsylvania State University’s University Park campus. To adapt to the huge growth in enrollment, the course was redeveloped in stages over several semesters to create hybrid and online versions of the course. The evaluation model was also changed to shift focus away from periodic examinations to weekly assessments. Students completed end-of-semester teaching evaluations for the course, and some students also participated in focus groups to discuss the effectiveness of the course redesign. Student evaluation results showed statistically significant improvements in student evaluation scores in all areas evaluated except for those areas that related specifically to the course instructor. The results of this study demonstrated that flipped classrooms can not only help programs to manage their introductory programming course enrollments, but they also increase students’ perceptions of the quality of courses.
Asad Azemi
B.3.2
The Pennsylvania State University, Brandywine
Changing Perceptions of Mathematics through Interventions in Introductory Freshman and Sophomore Levels Engineering Courses – 21009
In this work, we present development of a sequence of interventions in introductory freshman and sophomore levels engineering courses to bridge the gap between math and its relationship to engineering problem solving. This is in response to the following identified needs: (1) poor perception of math in general and calculus in particular among freshman engineering students, and (2) lack of adequate hands-on engineering content in freshman and sophomore level engineering courses. The interventions consist of number of projects with the goals of (1) to bring context and situate calculus and trigonometry concepts as being central to solving engineering design problems, and (2) improve students’ perception of mathematics as a problem solving tool. In addition, we will simultaneously assess the cognitive objectives of the project, based on an explicitly laid out rubrics, as the intervention is being conducted. The affective objectives will be subsequently measured in selected calculus intensive junior level engineering courses. Those courses are known to be as challenging subjects to teach due to the students’ poor attitude toward calculus, and lack of engagement and motivation. There are two main aspects to our proposed approach, the combinations of which we believe uniquely distinguishes our work from prior efforts. The approach only modifies content in existing design and computer programming courses outside the calculus sequence and will not involve creating new courses, and it will be a sustained effort through the freshman and sophomore years to emphasize and reiterate math concepts in courses concurrent with the traditional calculus sequence.
Yue Hung
B.3.3
State University of New York, Farmingdale
Enhancing Freshman Learning Experience in Computer Aided Drafting and Design (CADD) Through Applied Learning Experiences: Connecting the Dots – 21015
Engineering design is an integral part of the freshman learning experience in mechanical engineering and mechanical engineering technology programs. Not only it is important to teach students the concept of design, it is also important for them to be able to “connect the dots”; by being able to apply tools, skills, and knowledge they gained, in design projects as well as in other engineering courses. A great way to achieve this goal is through applied learning experiences. Applied learning is an instructional approach that includes various methods of teaching such as: project-based learning, hands-on learning, experience-based learning, service-learning, etc. In an effort to provide freshman engineering technology students an applied learning experience, two innovative approaches have been developed and implemented to the freshman level Computer Aided Drafting and Design (CADD) course. The first approach is the incorporation of hands-on exercises that follow Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy. The second approach is the development of a learning community where it is built focusing on the Computer Aided Drafting and Design and Manufacturing Processes courses. This paper provides an overview of the two approaches including their objectives, exercises, projects, and future plans. The design and development of the exercises and projects will be discussed in detail.
Tak Cheung
B.3.4
CUNY Queensborough Community College
Linking facts with judgment: a critical thinking component in introductory calculus physics for engineering students – 20999
Critical thinking has been summarized as an objective analysis of facts with judgment in popular open access platforms such as Wikipedia. The problem solving skill in terms of algebra and calculus are often perceived as facts by students with the necessity of memorization, while the judgment learning for engineering students includes extensions to other examples with the linking of the known facts and the given information. An E&M example is discussed as the following. The vector cross product embedded within the Biot Savart law could be solved with trigonometry given the underlying symmetry and/or with the 3-dim vector notion system. The judgment for applying the vector notion system is beneficial when it comes to the asymmetry Biot Savart law situation of a straight current-carrying wire and a current loop, acting a precursor to the conceptual understanding of magnetic reconnection at introductory calculus physics level.
Kimberly Riegel
B.3.5
CUNY Queensborough Community College
Qualitative content analysis of lab report discussion in introductory physics for engineering and technology students – 21000
The discussion section of a student’s of lab report have been assessed with the Mayring methodology and associated software for qualitative content analysis. An example of the categorization and coding procedure is discussed via a lab example of energy conversion from potential to kinetic. The software results were tabulated using the Torrance Creativity Test criteria to evaluate qualitative content in terms of critical thinking and creativity. Furthermore the Torrance scores were used as inputs into a causative structure model to assess “Learning with Intent”, together with “Critical Thinking” manifested in calculation tasks. Although the Intent Aptitude assessment model would require more data collection to confine the loading value of the Critical Thinking Aptitude onto Intent Aptitude, the combination of Mayring methodology and Torrance Creativity Test has been shown to be a working platform for assessing the writing content qualitatively in introductory physics for engineering and technology students.
Abdullah Konak
B.4.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Fostering Interest and Knowledge in the Information Security Industry for K-12 Students Using Virtual Machines – 21061
The field of information security is growing rapidly as malicious attacks to information systems become more frequent and detrimental to individuals and organizations who have become increasingly dependent upon these systems. With such a dramatic growth in demand in a short timeframe, there exists a shortage in the supply of professionals entering the field. In order to assist in the remediation of this gap, the Penn State Berks Information Sciences and Technology (IST) and Security Risk Analysis (SRA) programs are hosting an annual NSA and NSF sponsored summer camp as part of the GenCyber program. This camp is focused on critical thinking, problem-solving, and igniting interest in information security and other STEM fields through the application of hands-on activities in the security of a virtual machine environment. By implementing this program, Penn State Berks aims to show students the value of information security as early as reasonably possible, share the knowledge of safe practices and principles for using the Internet safely, and instill an interest in cybersecurity, as well as the STEM field as a whole. The evaluation of the program shows that the participants make significant progress towards achieving the learning outcomes of the summer camps.
Steven Barton
B.4.2
CUNY Queensborough Community College
Cosmic ray detection and magnetic cloud volatility analysis suitable for high school student research – 21004
The QuarkNet is an association of Femi National Lab physicists, college physics professors and high school physics teachers with multiple missions which include enhancing science and engineering knowledge through hands-on experience among high school students. Besides building cosmic ray detectors, we instituted a related activity in the studying of cosmic ray and/or solar proton induced muon production. This activity concerns whether the muon flux fluctuation has a relationship to solar eruption event effects. Mathematical skills at the pre-calculus level in the high school curriculum was found to be sufficient to perform the necessary analyses. A magnetic cloud event detected by the ACE spacecraft on April 14-15, 2013 was analyzed and the results were published on open access platform accessible by high school teachers and students. Our results, using basic spreadsheet tools such as copy-paste and histogram utilities, showed an increased volatility during the above mentioned magnetic cloud event in the Athens cosmic ray data available on the internet. The volatility histogram technique also revealed a solar proton peak event detected by the GOES-13 spacecraft the following day. Together with the sub-minute time resolution capability of the QuarkNet detector, future muon fluctuation volatility analysis by high school teachers and students for solar event analysis projects is discussed.
Rajarajan Subramanian
B.4.3
The Pennsylvania State University, Harrisburg
STEM Awareness Starts at the Elementary and Middle Schools – 21053
Is there a shortage of talented workers in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) in America? Yes is the answer to this question when various statistics of data are considered from different authentic government sources. Then the next question is how do we increase the STEM skills among the young Americans who pursue their K-12 education? Policymakers and School administrators across the nation have embraced the slogan “STEM” (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) but there is lot of confusion as to where to start the K-12 academic curriculum. This paper explores the different case studies and literature data available up to date to figure out how the importance of STEM education can be instilled in the young minds of K-12 school system. The author strongly feels that the STEM education should be started at the Elementary or Middle School level covering the first to eighth grade students based on the fact the young minds can be easily groomed at the very early age.
Emily Alexandra German
B.4.4
Vaughn College of Aeronautics and Technology
Initiating Engineering Learning for Minority Students in Elementary Schools – 20982
Efforts to raise student interests in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) careers have increased in recent decades. The goal of such efforts is to satisfy the urgent need for scientists, engineers and technologists due to the consistent growth of innovative engineering products, such as smart phones, autonomous vehicles and so on. Educational researches show that the efforts to interest students in STEM majors and careers can be as early as in the elementary school level, the time when students begin to develop interests in engineering products around them. In this paper, we present one approach towards organizing an engineering workshop for elementary school students, particularly minority students, by educating them on how to build an engineering product: a speaker. After the workshop, the students not only learned the basic concepts of engineering and engineering product development, but also held and enjoyed a self-made product at home. The students’ responses indicate that while they had fun building the small device, they also understood the essential process to design and implement an engineering product. This could be of significance for them to gain an interest in engineering and eventually choose it as their future career.
Ryan Scott Hassler
C.1.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Engineering Ahead: A model for increasing retention of underrepresented students in engineering – 21005
Engineering continues to remain one of the highest demand jobs in the US, as colleges and universities are not producing enough applicable graduates. This problem appears to be two-fold: recruitment and retention. Recent research suggests that only between 1 and 2.5% of secondary students show interest in STEM related careers and only 60% of students who enter college with an intended engineering major actually earn an engineering degree. Of those who do complete the degree, only about 12% are from underrepresented populations, which creates an engineering workforce comprised of only about 13% females, 5% African-American and 6% Latinos. This study examines how an NSF funded four-week summer bridge program (Engineering Ahead) attempts to answer the urgent need for increasing retention of underrepresented students in engineering. Engineering Ahead revolves around intense exposure to Pre-Calculus topics and aims to create an academic learning community for freshmen engineering students from diverse socio-economic and cultural backgrounds. Details surrounding mathematics content and academic success building skills used in the program will be discussed. Overall measures observed from the first two cohorts of students indicate positive results. Qualitatively, upon completion of the program, students noted how prepared they felt for their first semester. Many specifically commented on how beneficial it was to review basic mathematical methods used in engineering, which supports the statistically significant differences found among their pre- and post-test assessments. A review of first semester math grades and overall GPA’s from the first cohort of participants, further suggest the effectiveness of Engineering Ahead.
Robert L. Avanzato
C.1.2
The Pennsylvania State University, Abington
Improving Student Engagement in Online Engineering Courses using Virtual Environments – 21018
The benefits of online learning include asynchronous access to learning resources, flexible scheduling, meeting demands of non-traditional and adult students, multi-campus and international participation, and accommodating learning preferences for many students. Some of the challenges of online learning include student isolation, difficulty communicating and collaborating with other students on team projects, and challenges in engagement and in the effective presentation and sharing of team projects. This study evaluated the use of Terf® (3D ICC) virtual world technology to support student communication, collaboration, and engagement in an online undergraduate, sophomore-level computer engineering course in digital design and also in a computer science course for engineers. Virtual world technology provides a persistent 3D immersive environment in which students and faculty log into the platform with personalized avatars and enter customized virtual workspaces that support avatar navigation, text chat, voice communication, shared resources, and a webcam. Most importantly, the Terf® product allows student teams to work collaboratively on shared documents and images, facilitating team projects and improving student interaction and communication. The virtual collaboration tool also supported interaction with 3D models, virtual office hours, virtual lectures, and a team final project virtual poster session. Overall, the feedback from student surveys was positive and the students judged the tool as beneficial to improving student interaction, engagement and collaboration in the online courses. A demonstration of the software will be provided as well as future directions.
Erin A Hostetler
C.1.3
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
Housing REU Programs in the Engineering Diversity Office: Increasing Retention of All Students – 21007
Diversity on campus benefits all students. Learning with people from a variety of backgrounds encourages collaboration, fosters innovation, and increases retention. However, the student body commonly underutilizes the resources and services provided by the diversity office. At Penn State University, a non-traditional model was created in the College of Engineering’s diversity office by placing the unit that focuses on research and student engagement experiences for undergraduates in the Center for Engineering Outreach and Inclusion. The common thread for all divisions within the Center is a focus on student retention. The association gives the Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) programs an intentionality and sensitivity to issues around diversity, and it gives all students in the College a visible access to the services facilitated by the Center. Primary results from the foundation of Student Research and Engagement as a part of the Center for Engineering Outreach and Inclusion show that the REU programs are effective tools for retention. Additionally, there has been an increase in all students utilizing services of traditional diversity service units, increased collaboration within the Center, better student referral to resources such as funding, and an increase in students participating in research across all demographics.
Joseph Michael Mahoney
C.2.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Case Study of a Video Game Design & Development Course for Mechanical Engineers – 20980
Anecdotally, it has been observed that many engineering students are not motivated to learn or apply computer programming in their courses. Possibly, this is due to computer science topics being pushed upon them rather than students learning them as needed. A senior-level video game design class was offered as a technical elective. This class combined a “humanities” viewpoint of video game design (e.g. gaming psychology, theory of fun) with the “technical” side of computer programming and physics engines. Students compared and contrasted two games and wrote a critical analysis of a game. The majority of the class was spent conceptualizing, planning and creating a video game. Groups learned the required programming skills as needed to implement their vision. Students completed a survey at the conclusion of the course. Generally, students found the course exercised their creative skills, motivated them to learn more programming and provided them experience in project management.
Christian Enmanuel Lopez
C.2.2
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
Towards Real-time Ergonomics Feedback and Educational Content with the use of Co-Robots – 21017
Engineering students will play a major role in the process of improving the ergonomics in the workplace. Nonetheless, studies indicate that engineering students are not familiar with the Human Factors & Ergonomics (HF&E) methods used to improve these systems. Therefore, more emphasis should be given to advance HF&E education. However, in this pursuit hands-on activities that promote active learning need to be encouraged in order to maintain students’ satisfaction and motivation. Moreover, the initial results from the case study presented in this work indicate that students’ HF&E knowledge needs to be improved, and that they frequently use improper lifting techniques. In light of this, the recent advancements in technology, that could potentially allow a Co-robot system to provide real-time ergonomic feedback and HF&E educational content to students, are explored. Such a system has the potential to help students better understand and experience firsthand how HF&E can be applied to improve the workplace. Even though the method proposed is in its initial design stages, its capabilities are promising and future work will focus on implementing the system in engineering lab environments.
Ge Jin
C.2.3
Purdue University Northwest
PNW GenCyber Summer Camp: Game based Cybersecurity Education for High School Students in Chicago Metropolitan Area – 20981
Cybersecurity is critical to the national infrastructure, government, military and industry. To defend the U.S. against the cyber threats, a significant demand for skilled cybersecurity workforce is predicted in government and industrial sectors. To address this issue, Purdue University Northwest has successfully launched four GenCyber summer camps for 181 high school students in Chicago metropolitan area to stimulate the high school students’ interest in the cybersecurity field and raise their awareness of cybersecurity and safe online behavior. PNW GenCyber summer camp activities were delivered in the format of game based learning and hands-on labs. The use of game-based learning in the camp was an excellent platform to teach concepts of cyber security principles. Game based learning provided an immersive, learner-centered experience to high school students, which has been proven to be very effective on cybersecurity awareness training and practical skill acquisition for learners from diverse backgrounds.
Matthew Rhudy
C.3.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Relationship between Voluntary Graded Homework Assignment Pickup on Exam and Course Performance – 20972
Student performance depends not only on their intellectual ability, but also their habits and decision making. Homework assignments can directly affect student performance in a course, but also indirectly through preparation for exams. This is specifically prevalent for engineering courses which involve homework assignments as practice problem sets to prepare for examination questions. This work investigates the differences in grade performance between two student groups within an engineering dynamics course: those who voluntarily picked up a graded homework assignment prior to an exam, and those who did not. Results from this research effort indicate that on average students who picked up their assignment performed better on the assignment, the midterm exam, and the overall course grade, however statistical significance was only found for the final course grade.
Matthew Jason Bilsky
C.3.2
Lehigh University
A Preliminary Investigation into the Use of Audience Video Recordings to Assess Student Engagement During in Large Lecture Classes – 20992
Twenty-first century higher education is moving from a faculty-centered teaching model to student-centered learning. With this change the question has become are the students learning? This study presents a method for direct, authentic, and formative assessment of the student engagement level during various lecture techniques in large classes. The basis for this study is that student engagement leads to student learning. Video recordings of a 208-student capstone lecture audience were assessed for five different lectures using an ordinal scale. Three different pedagogies were explored: traditional lecture, active-collaborative learning (ACL), and random calling to see if they have an effect on the average level of engagement during lecture. It was shown across 59 data points that ACLs lead to a significant increase in engagement while there is no meaningful difference between traditional lecture and random calling especially when compared to ACLs.
Alex C. Szatmary
C.3.3
King’s College
Student analysis of survey of student skills to enhance confidence – 21055
This study was done on a first-year class entitled “Computational Analysis” (CA) at a liberal-arts university in the Middle-Atlantic region. The content of CA focused on using computer tools such as spreadsheets and programming to solve engineering problems. No previous experience in writing code was expected but some students did have skills in writing code. To determine the range of students’ prior experience with computing, I administered a survey at the start of CA. Students described the extent of their previous experience with Excel and programming as well as their level of confidence with each of these. I also asked about whether students knew how to use certain programming constructs. On the survey, several students expressed concern that their lack of experience with programming would cause them to be left behind relative to their classmates. From the survey data, there was no correlation between self-reported confidence in ability to use Excel versus to write code. Because analyzing data in Excel was a course goal, and to alleviate student concerns about differences in preparedness, I developed an in-class activity in which I provided the anonymized survey data to students who then analyzed the data and completed a survey in which they discussed the findings. On this second survey, students stated that they felt less alone and worried and that they were reassured that many of their classmates actually had similar levels of preparation. Unfortunately, one student’s perception that they were less prepared was actually reinforced.
Ashwin Satyanarayana
C.3.4
New York City College of Technology
Common Assessment of Two Related Courses to Reduce Grading Bias and Improve Readiness of the Students for Corporate Environments – 21067
This paper presents an approach to assess students attending two related computing courses. To demonstrate our approach, we evaluated students taking either Fundamental Networking or Fundamental Database courses. Towards the end of the semester, students taking both courses were asked to individually finish a common term project resembling a scenario in the corporate environment. One of the objectives of this assignment was to let students recognize benefits of mastering different but related areas of study. Another goal was to teach them that various computer technology courses are interconnected and that a computer specialist can use skills learned in one area to better understand concepts of the other one. The students were evaluated based on their abilities to combine knowledge from the subject they studied with researched information about a related area in computer technologies. Each student’s project was assessed by two professors and the results were analyzed to better prepare future interdisciplinary assignments while eliminating potential grading bias. This type of assessment methodology could benefit students, by introducing them to advantages coming from broader knowledge, and educators, by letting them develop cross-disciplinary assignments that are resilient to instructor’s grading bias while stimulating students interests.
Michael Lawrence
C.4.1
Queensborough Community College
Lessons Learned In Promoting STEM With 3D Printing If you build it (the lab) will they come? – 21060
Queensborough Community College (QCC) is one of 26 campuses of the City University of New York (CUNY). It is a 2 year college, Minority Serving Institution (MSI), in New York City with 16,000 students. One year ago QCC installed a $2MM Advanced Manufacturing Lab with high-end 3-D printers. This paper outlines the lessons learned in fostering STEM Adoption during the Lab’s first 12 months of operation. Our first year results, while modest, are encouraging. 1 student hired by an additive manufacturing company, 1 student interning at a global medical research center, 1 peer learning project, and 4 students participating in MESIP Grants. The topics covered will include 1) goal & objective setting, 2) stakeholder analysis and engagement & 3) student outcomes and learning objectives. Goal & Objective Setting – What we found to be reasonable goals in reasonable timeframes. Stakeholder Analysis & Engagement – How we approached: Student adoption, Faculty adoption, External industry partners, External academic partners, College leadership, and College legal. Student Outcomes & Learning Objectives – The what and the how of our student learnings.
Jason Lehrer
C.4.2
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
The Development of a Sustainable Technology for 3D Printing Using Recycled Materials – 21044
As part of an undergraduate research project, a study was undertaken to determine the feasibility of extruding recyclable plastic into usable filament to create a sustainable technology for 3-D printing. An extrusion process was developed using PETG pellets to create a baseline that would be used when incorporating recyclable plastics. Modifications were done to allow for higher temperature extrusion to accommodate the higher melting temperature of PET plastics. A method of drying the plastic prior to extrusion was determined to be a necessary factor in the extrusion process. The viscosity of the PET plastic was determined to be a valuable characteristic that affects the possibility of creating filament. From this study, a conclusion can be made that there are multiple key factors that will determine the feasibility of extruding recyclable plastics into filament.
James J. Scire
C.4.3
New York Institute of Technology
Dynamic Balancing System with 3D-Printed Components – 21016
This paper describes a project in which students designed, built, and used a small dynamic balancing machine with 3D-printed components. This project was found to be very effective in keeping its student designers engaged and invested. They immediately understood the need for balancing, and they had an opportunity to apply simple concepts from mechanical vibrations, linear algebra, and electronic circuits to complete this task. Construction details and the results of balancing a small rotor are presented.
Yong Zhu
C.4.4
Wilkes University
Design and testing of a low cost home companion robot – 21021
To reduce the cost of health care and improve the quality of life of elderly people, more and more robots are being designed to interact with a human being to provide affordable and robust care at home. Imagine a home companion robot like Baymax from “Big Hero 6” that could follow you around your house, talk to you and even observe your facial expression. The goal of this project is to develop a small home companion robot that could eventually provide elderly companionship and help with daily activities. A Pixy vision sensor (CMUcam5) is used to provide fast vision feedback to the Arduino microcontroller so that the robot can interact with its user and environment. Satisfactory results were collected for the robot and the robot’s interaction with the surrounding environment. The robot was able to autonomously navigate around the surrounding environment at its own discretion. The robot was also able to follow a person using the camera interface and a color code. Finally, the robot was able to have a small speech functionality via a speaker. Overall, the concept was proven to be effective through trials. It would have great potential to be used as an intelligent, low cost home companion robot to provide some of the elderly care that traditionally can only be provided by a home care provider. Ultimately, the home companion robot would be able to navigate autonomously in typical home environments to perform tasks such as smart medicine reminder, daytime activities manager, autonomous docking and recharging etc.
Ivan E. Esparragoza
D.2.1
The Pennsylvania State University, Brandywine
Assessment of Progressive Learning of Ethics in Engineering Students Based on the Model of Domain Learning – 20989
This work presents the results of an assessment instrument designed to assess the progressive learning of ethics in the engineering curriculum at different stages known as acclimation, competency, and proficiency, and to determine the relation of the development stages with three components that contribute to learning: interest, knowledge and strategic processing. The questions in the instrument were defined following the Model of Domain Learning (MDL) to capture the level of ethics skill development. The questionnaire was administered to engineering students of increasing class standing (i.e., freshmen to senior). The results show that the instrument successfully captures the ethics skill development in engineering education taking into consideration the components and stages of learning described by the MDL framework.
Christine Masters
D.2.2
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
A Conversation About Academic Integrity (Discussion Panel) – 22000
Please join Christine Masters and your ASEE colleagues for an informal discussion about Academic Integrity in engineering courses. Chris will give a very brief presentation in the Penn State process for handling Academic Integrity violations as well as a few things she has tried to deter cheating and promote Integrity. But the majority of the session will be a facilitated discussion among the attendees. Come to share your experiences or just hear about the experiences of others. Chris has extensive experience on all sides of the Academic Integrity issue:
- instructor of both small (40) and large (600) classes, bringing forward multiple violation cases each of her 12 years in teaching
- consultant to peer department faculty encountering their first case * advocate to help students in the department navigate the process who felt wrongly accused by another instructor
- member, chair, and now facilitator of the college-wide Academic Integrity committee. At Penn State, Chris is the Assistant Dean for Academic Support and Global programs in the College of Engineering and Associate Professor of Engineering
Shane Rogers
D.3.1
Clarkson University
Exploration of ASEE Board of Directors Reorganization (Discussion Panel) – 22100
Jason Jiang
P.01
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
A Prototype Cybersecurity Virtual Network Laboratory for Smart Grid Cybersecurity – 21001
In order to improve the reliability and efficiency of the electric grid, information technology (IT) systems have been increasingly integrated into its operations at different levels, from power generation to distribution, and to consumption. Integration of digital communications networks, data acquisition devices, intelligent control systems to an electric power grid is called smart grid. There is a growing concern that if smart grid technologies are not implemented securely, the electric grid itself would become more vulnerable to cyber attacks. One major concern is the vulnerability of devices at the customer premise such as smart meters that enable real-time interaction between the customer and the utility management system. While it is an important need for the U.S. electric utilities to have access to a talented pool of individuals who are trained in confronting cyber threats to smart grid technologies, the capability of providing such education is limited. First of all, any cybersecurity education must rely on practical “hands-on” experience in secure networking environments to test critical tasks. This paper focuses on building the capability to provide experiential learning in smart grid cyber security by integrating virtual and physical laboratories. Specifically, a virtual computer laboratory for smart grid penetration testing is introduced.
Michael R. Bartolacci
P.02
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Preventing PDOS Attacks on Campus – 20990
This work brings to light the current attitudes and practices of university students regarding the intentional disruption of online services of their peers. This type of disruption on a campus was previously termed a PDOS or Personal Denial of Service Attack where a student utilizes the security of websites and online accounts to prevent another student from accessing such . I bring forth several points that should be addressed in entry level computing courses in order to reduce the severity and frequency of such attacks. By providing students with the basic knowledge of how easy it is to conduct such an attack (and to prevent it) in introductory computing courses, they can reduce the likelihood of being a victim of such an attack.
Dorothy Carter
P.03
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
Silk and Zingerone: A Novel Marriage for Bone Grafts and Bone Growth – 20971
Tissue engineering plays a critical role in regenerative medicine and utilizes a combination of stem cells, suitable biocompatible scaffolds, and interactions between biochemical factors to analyze cell mobility and cell interactions. This project, aimed at creating bone grafts for bone regeneration, analyzes the interplay of a chemically tunable silk scaffold, isolated from Bombyx mori, with functionalized microspheres encapsulating Zingerone. This unique structure is designed to act synergistically as a suitable architecture with the necessary mechanical properties and biological features needed to promote bone growth while attenuating factors relevant in osteoporosis. The result of this project will have an impact on bone regeneration needed as a consequence of either degenerative diseases or low-density bone resulting from the aging process.
Nicholas Patrick Haring
P.04
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Critical Thinking and Entrepreneurship K-12 Workshops – 21051
It is imperative that Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) graduates are prepared for complex social, economic, and technological problems of the 21 Century. It is also crucial to encourage younger students to build an entrepreneurial mindset, as they are inevitably the entrepreneurs of the future. Hosted by Penn State Berks Entrepreneurship students and faculty, middle and high school students in Reading, PA are able to participate in entrepreneurial workshops every semester. Concepts such as value creation, idea generation, and critical thinking are taught by student mentors during each semi-annual workshop. The objective of the workshop program is to develop an entrepreneurial mindset in youth through hands-on creative problem-solving activities. After these activities, workshop attendees are tasked with creating their own business from scratch. This includes how the business would operate, where and how they would obtain their resources, what sets them apart from their competitors, and many other aspects. The feedback to our pre and post surveys obtained from the participants has shown that the students feel more excited and interested in entrepreneurship after participating and therefore the workshop is effective in teaching them how to develop and expand their entrepreneurial mindset through creativity and creative problem-solving activities.
Baha Bachnak
P.05
The Pennsylvania State University, Harrisburg
Developing Lab Exercises for Logic Circuit Design using FPGAs – 21054
An introductory course to digital logic design is a requirement for most electrical and computer engineering (ECE) programs. It is also one of the first technical courses that ECE students are exposed to. Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) is a versatile and adaptable technology with many applications ranging from medical image processing, to cryptography. Colleges and universities struggle to maintain a feasible four-year program for students due to advances in technology and the need to incorporate new concepts. By combining an FPGA course and a digital logic design course, the number of required credits may be reduced. This paper reviews a number of academic approaches to incorporate FPGA design in digital design courses and presents a number of laboratory experiments (tutorials) that paves the pathway for designing a sophomore-level four semester credit hour (SCH) course.
Chris R Fatzinger
P.06
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Carbon Fiber Composite Wings for Flapping Mechanism – 21022
The design of flapping wing devices is an active research area [1]. There are currently no manned flying vehicles that utilize flapping wings as the source of lift and thrust. However, all birds and insects utilize this naturally, as a means of near effortless transportation. Flapping wings can be mimicked, by copying the structure of a bird’s wings. This study explored the use of carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites for lightweight and durable flapping wings. The carbon fiber polymer matrix composite utilizes carbon fiber for the strength, and the epoxy for the structure of the composite [2, 3, 4, 5]. The objective of this project is to determine the size, shape, and structure of CFRP wings appropriate for a flapping device to produce enough lift. Several composite wings are built and are ready to test. The first design is a simple sheet of CFRP, that has no structure to it. The second design is made of two pieces of CFRP, which is connected by two elbowing hinges. The third design is also two sheets of CFRP connected with elbowing hinges, but has a spar layout to mimic the shape of a dove’s wing. The final design is two pieces of CFRP connected with elbowing hinges, using a second ply as the reinforcing structure. The testing will be done using a multi-axis force sensor attached to the flapping mechanism.
Cory David Jamieson
P.07
The Pennsylvania State University, Dubois
Tensile Properties of Dielectric Elastomers – 20995
As the demand for energy continues to grow, we look to improve the transport processes to ensure the longevity of our investment and to elevate the energy system as a whole. One way to improve energy transport is through the use of cable insulation to isolate the transmission from outside interferences. Many types of materials are used for cable insulation, the goal of this project is to understand how processing and curing can effect elastomers, specifically low density polyethylene (LDPE) and crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE). This will be done by creating thin films of both LDPE and XLPE with the ability to control pressure and temperature during melt processing. After fabricating thin films, each sample was examined to establish the individual micro structure, with further investigation comparing LDPE and XLPE’s mechanical properties. Material selection and the dimensions of that material are critical to prevent failure during application. Tensile testing can help identify three fundamental mechanical properties, the modulus of elasticity, yield point and ultimate tensile strength. These properties are then used to determine what material or if a material is best suited for a specific job based on practicality and cost.
Jesse Wengel
P.08
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Fundamental Fluid Dynamics of Flapping Wings – 21014
Flapping wings generate lift and thrust through an incredibly complex set of choreographed movements coupled with micro-adjustments occurring as often as many times throughout a single stroke of the wing. These types of wings come in various shapes and sizes; eagles’ wings are significantly different from dragonflies’ wings, for instance. Humanity’s understanding of flapping wing aerodynamics has increased dramatically over the past few decades – from not being able to accurately calculate forces generated by such wings, to building insect-sized robots that can fly almost as well as their biological inspiration – but there is still much room for growth in this field. This study intends to scrutinize the fundamentals of flapping wing fluid flow phenomena in order to establish a foundation for more complex studies in the near future. The first experiments will consist of the simplest case possible: a flat rectangular plate with rounded edges in plunging-only (up and down) motion with two-dimensional fluid flow around the wing’s cross-section. These experiments will be conducted by placing a plunging wing apparatus, designed and built in-house, into a water channel with dyes injected upstream from the wing. Particle image velocimetry will then be used to photograph the leading and trailing edge vortices generated by the wing, and these vortices will be analyzed with respect to Reynolds number and other fluid dynamics parameters. Next steps for this project consist of machining and assembling the designed apparatus, finalizing the motion controlling program, and finally performing experiments and analyzing the data. This research and its successive investigations may eventually lead to more efficient or better-performing aircraft, along with a better understanding of naturally-occurring wings.
Sachin P Patil
P.09
Widener University
Cancer Immunotherapy- Discovery of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of PD1-PDL1 Interaction – 21037
The protein-protein interaction between PD1 and PDL1 proteins expressed by immune T cells and cancer cells, respectively, is one of the critical pathways utilized by tumors to escape their destruction by the immune system. Therefore, inhibition of the PD1-PDL1 interaction presents a fundamentally novel therapeutic strategy to activate innate immune system against a variety of tumors. Accordingly, five antibodies that inhibit PD1-PDL1 interaction have been recently approved and several are in clinical trials. In contrast, despite their inherent pharmacokinetic advantages, there are no approved small-molecule inhibitors of PD1-PDL1 interaction so far. Few such small-molecule inhibitors are reported in the literature, but most of them have relatively modest or weak activities, emphasizing the difficulty in designing small-molecule inhibitors against this challenging protein-protein interaction target. In this context, we undertook a multi-disciplinary approach in discovering small-molecule PD1-PDL1 inhibitors through integrated computational and experimental screening of the National Cancer Institute compound database. Specifically, a high-throughput virtual screening of a database containing ~100,000 drug-like compounds was followed by the experimental testing of few top virtual hits. This led to the identification of several compounds, with the most active compound exhibiting 50% inhibition of PD1-PDL1 interaction at only ~15 microM test concentration. This is a remarkable activity considering these compounds have low molecular weights and still are capable of inhibiting PD1-PDL1 protein-protein interaction with very large binding interface of ~1,970 Å2. In summary, our newly-discovered compounds may prove highly suitable for further optimization into more potent, selective inhibitors of this traditionally challenging, but clinically-validated promising anticancer target.
Ryan Blankenbiller
P.10
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Producing 3D Casts With Use of a Kinect Sensor – 20993
The purpose of this study was to determine the feasibility of creating a 3d printed cast from a scan obtained from a scan with a Kinect sensor. Skanect, a scanning software, allowed for the retrieval of a scan from a Kinect sensor. Meshmixer, an editing software, allowed for manipulation of the scan into a customizable outer shell of the arm. A two piece design including a Voronoi pattern was then printed. The resulting print was compared to the limb that was scanned to test the viability of scanning and using a 3d printer to create a solution for the healing of a broken limb in the orthopedic setting.
Angela Davis
P.11
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
Literature Used in Nuclear Engineering Dissertations: A Citation Analysis – 21010
Analyzing the bibliographies of dissertations provides a wealth of information that can be used to determine research trends, evaluate instructional needs of students, and usefulness of library collections. Dissertations are published to fulfill PhD degree requirements; their purpose is to add new knowledge to a field of study. This requires students to do extensive research. The author studied nuclear engineering dissertations published between 2010 and 2015 in the United States. Approximately 100-200 dissertations were published each year which resulted in a national but manageable sample for analysis. These citations were analyzed to answer the following questions: 1) Which reference formats are used in nuclear engineering? 2) What is the age of the cited items? 3) Do citation patterns vary over the years studied. A format of particular interest is technical reports. Technical reports describe the process, progress, or results of technical or scientific research and are a preferred form of scholarly communication for engineers. The Penn State Engineering Library holds a large collection technical reports that is largely hidden due to inadequate cataloging. In order to determine if staff resources should be spent to make this collection more accessible, an analysis of the usage of these materials was conducted. This poster will explore the three questions, with a focus on technical reports, to draw conclusions that will aid researchers in exploring the range of scholarly sources available and librarians with decision making on resources to make accessible.
Gabriela Gonzalez-Magana
P.12
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Human Emotion Recognition through Different Real-Time Sensors that Measure Physiological Signals – 20979
Emotions are an important part of human interactions with the world. Individual human emotions can lead to both positive and negative outcomes; however, it is almost unknown how human emotions can be recognized through physiological signals. Therefore, in this study we focused on information about how human emotional state is communicated through observable physiological signals. The Empatica E4 wristband device is used to measure physiological signals that determine human emotions through multiple sensors in real-time. The Photoplethysmography sensors (PPG) from which Heart Rate and Inter-Beat-Interval signals are derived, the Electrodermal Activity (EDA) for skin conductance, optical Temperature and 3- axis accelerometer for movement activity. Different signals will determine when the person is experiencing different emotions or being physically active. The changes in Electrodermal Activity (EDA) and Heart Rate (HR) signals were noted for emotional states. Physical activity patterns can be easily recognized through acceleration and heart rate signals.
Mpila Makiesse Nkiawete
P.13
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
Study of Porous Carbon Materials for use as Electrodes in Capacitive Deionization of Salt Water – 21069
Capacitive deionization is an efficient and economical desalination technique. With the current water demand for irrigation and the need for the conservation of drinking water, capacitive desalination of brackish water offers an alternative way to reduce the tension between irrigation and the direct consumption of water. This research comprised of carbon production, activation, characterization, electrode fabrication, electrochemical testing and analyses for capacitive desalination rate, capacity and cycling stability. The electrodes were fabricated using various carbon precursors including commercially available activated carbon cloth, polyfurfuryl alcohol derived carbon and biomass (Coconut shell, Switchgrass) derived high surface area activated carbon materials. The goal of the research was to compare the adsorption rates and capacities of these carbon materials as well as their charge and regeneration efficiencies in order to determine which of the activated carbon material is best suitable for this technique. Our investigation showed that microporous coconut shell derived carbon had the best charge efficiency while polymer derived carbon had the highest adsorption rate. The pore size distribution of the carbon had a profound impact on the performance of the device. Microporosity in carbon helps to improve the salt adsorption capacity. Macroporosity provides transport and improves dynamics of adsorption however at the cost of charge efficiency. Among the carbons, YP50 had the highest charge efficiency of ~ 60% while PFA-PEG600 had the highest salt removal capacity of ~5 mg/g. Salt removal capacity increased with increase in voltage for all the carbons.
Caedmon DelVecchio
P.14
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Peer Evaluation and Assessment Resource – 21038
Peer evaluations usually reduce the teamwork related problems in term projects. However, peer evaluation is a time consuming process. In this paper, we present an online tool- Peer Evaluation and Assessment Resource (PEAR) that streamlines the work required to collect peer evaluations from students. One of PEAR’s greatest strengths is that it gives both the instructor and the student an intuitive web interface. Instructors can use this interface to create assessments with pre-configured or custom rubrics. After that is done, instructors can then use the system to add students and automatically send out emails to students. As students submit their evaluations, instructors can view the results for the whole class as well as for groups and individuals. This process greatly reduces the time required for instructors to create, distribute, and compile peer evaluations. In addition to this, students enjoy the ability to complete evaluations through a web browser instead of printed paper evaluations. PEAR gives both instructors and students a simpler and more effective way to conduct peer reviews.
Thomas Jones
P.15
The Pennsylvania State University, Berks
Comparing Efficiencies of Two and Three Bladed Multirotor Propellers in Crosswind Conditions – 21039
Technological advances have greatly contributed to the rise in popularity of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), specifically multirotors. Much is known on the efficiencies of various types of blade designs in large part from fixed wing aircraft propulsion. The efficiency tests for these blades is almost always conducted in air with the propeller disk facing a direct headwind, to simulate direction of travel of the aircraft. With multirotors, the path of travel is more robust and the vehicle has the ability to hover as well as travel in the direction it is tilted. It is because of this extra motion that the effect of crosswinds on the rotor blade must be accounted for. By testing the performances of a HobbyKing 13×5.5 inch two-bladed propeller and a KDE Direct 12.5×4.3 inch three-bladed propeller in a water channel, both the amount of thrust generated at given rotational rates and flow visualization can be found and observed. Thrust measurements are gathered by using a loadcell and revolutions per minute (RPM) are determined by using a high speed camera and counting rotations in a given number of known video frames. Through this method it can be determined which propeller is better suited to providing optimal thrust in a crosswind. This data can help multirotor manufacturers optimize their designs and allow for the possibility for software to take into account the added effects of crosswinds on the individual rotors when calculating total flight times.