This figure illustrates the Surface Radiation Budget Network (SURFRAD) meteorology of Penn State Pennsylvania. This data and plot was taken from the Earth Systems Research Laboratories website; https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/grad/surfrad/met_check.php
There are 5 mini plots within the large plot demonstrating different parts of climate over the last 24 days. Since it is nearly impossible to research the climate of every single place on earth, scientists created SURFRAD to help. SURFRAD picks up on different climate activity within a specific area to help researchers come to conclusions about the climate. In this SURFRAD plot the specific things being tested (from top to bottom) are the wind speed (mph), wind direction (degrees), temperature (ºF), pressure (mbar), relative humidity (%).
The multiple different parameters are important to global climate change because it gives specifics to all the different aspects that go into the climate. It is one thing to look at the temperature and how that has changed over time, being able to see all the different variables helps give more information towards the bigger idea. By looking at wind speed and direction, one can tell that over time it has been speeding up which is an indication of climate change. Temps, humidity, and pressure are rising all indications of climate change (Harvey 2019).
To add onto what was previously stated, the trends shown on the plot are clear indications of climate change. It is hard to conclude to that just by looking at plots that cover 24 days, but with further outside research one can see the patterns. This hurts humans because if temps keep rising, life forms will start to die and perhaps thousands of years from now the earth could become too hot that it is not livable conditions for humans (Harvey 2019). As the climate changes, the potential risks for humans increases.
References
Harvey, Chelsea. “The World’s Winds Are Speeding Up.” Scientific American, Scientific American, 19 Nov. 2019, www.scientificamerican.com/article/the-worlds-winds-are-speeding-up/.
US Department of Commerce, NOAA. “ESRL Global Monitoring Laboratory – Global Radiation and Aerosols.” NOAA Earth System Research Laboratories, 1 Oct. 2005, www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/grad/surfrad/met_check.php.








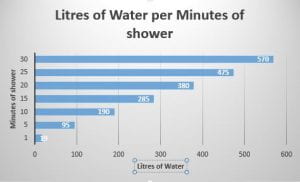

 This chart represents the ecological footprint of the country.
This chart represents the ecological footprint of the country. This chart represents the ecological footprint of each person in the country.
This chart represents the ecological footprint of each person in the country.