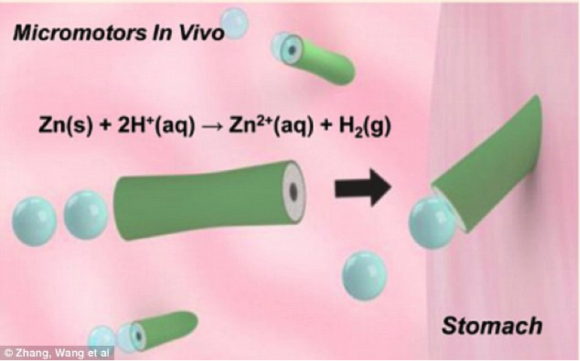
The hypothetical theory of using microscopic machines to deliver drugs in the human body may have just become a reality. For the first time, researchers have successfully used microscopic machines inside mice to deliver nano-particles to their stomach lining. The “machines” are made of polymer tubes and coated in a layer of zinc, which upon ingestion reacts with the stomach acid to produce hydrogen bubbles. These bubbles act as a motor and drive the machines to their end destination, which in this case was the stomach lining. When the machines finally reach their end destination, they attach and dissolve, releasing the drugs into that specific area.
The original means of drug delivery that we still use today usually involves orally taking a pill. What is inefficient about this is that the pill dissolves into the bloodstream, and as a result the drugs work on the entire body rather than a specific area. This is the reason why drugs oftentimes have many side effects. However, the method of using microscopic machines will be able to target exactly where the drug is needed. This will decrease the amount of time it takes for the drug to take action in addition to limiting side effects. Although this is the first time these machines have ever been used on living animals, it is a major step forwards in terms of the eventual goal of human application.
This is my last passion blog for the semester, so I wanted to briefly take a look back on all of the scientific advancements of the past year that I have blogged on. The subject of each and every post involved a technology that will contribute to living healthier and more fulfilling lifestyles. I have a passion for science and medicine because it is a continuously evolving field with endless possibilities. If society could do all this in just one year, imagine what the future holds as technology continues to improve.
This image shows how the microscopic machine reacts with the acid of the stomach to produce hydrogen bubbles, which direct the machine to its final destination where it attaches and releases the drug.
Source:
http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-2918010/Microscopic-machines-travel-inside-living-ANIMAL-time-one-day-used-deliver-drugs-inside-humans.html