I’m sure you’ve at least heard of the elusive blobfish. The name itself gives you a great idea of what this creature looks like: a blob of goop. The scientists in charge of naming it were clearly not thinking outside of the box. While many of the creatures covered on this list were enormous, terrifying, and dangerous, this specimen is none of the above. Allow me to introduce you to the blobfish: the world’s ugliest fish.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/Blobfish-ugly-470.jpg)
The blobfish is most famous for its hilarious appearance. It looks like a big, sad, droopy, squishy face. It looks like if Mitch McConnell was put in a vacuum chamber. The blobfish went viral on social media and was featured in countless memes due to its comical appearance. But is there more to this fish other than its looks?

There is actually a reason why the blobfish is so gelatinous and saggy. The blobfish resides at depths between 2000 and 4000 feet deep, where the pressure is much higher than on the surface. The creature’s bodily make-up is a result of thousands of years of evolving to survive the harsh conditions of the deep ocean.
The blobfish does not have bones, teeth, or much muscle mass. The crushing pressure of the ocean gives the fish enough support to not need bones. It is not a particularly active creature—spending most of its days looming above the ocean floor. Therefore, it does not need muscle.
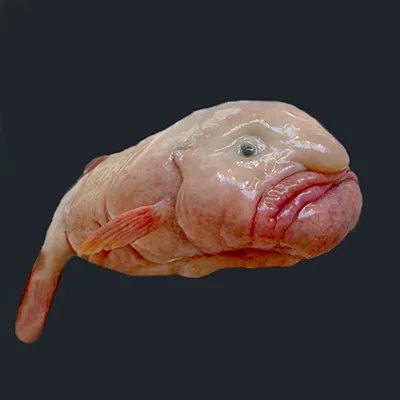
Instead, the fish is composed mostly of water-filled cells. This jelly-like tissue is less dense than water, allowing it to stay buoyant. Because it can float effortlessly, it can conserve energy in its habitat, which is scarce in food.
Who knew this ugly fish was actually an astounding example of evolutionary adaptation? When it is in its natural habitat, it even looks pretty normal.
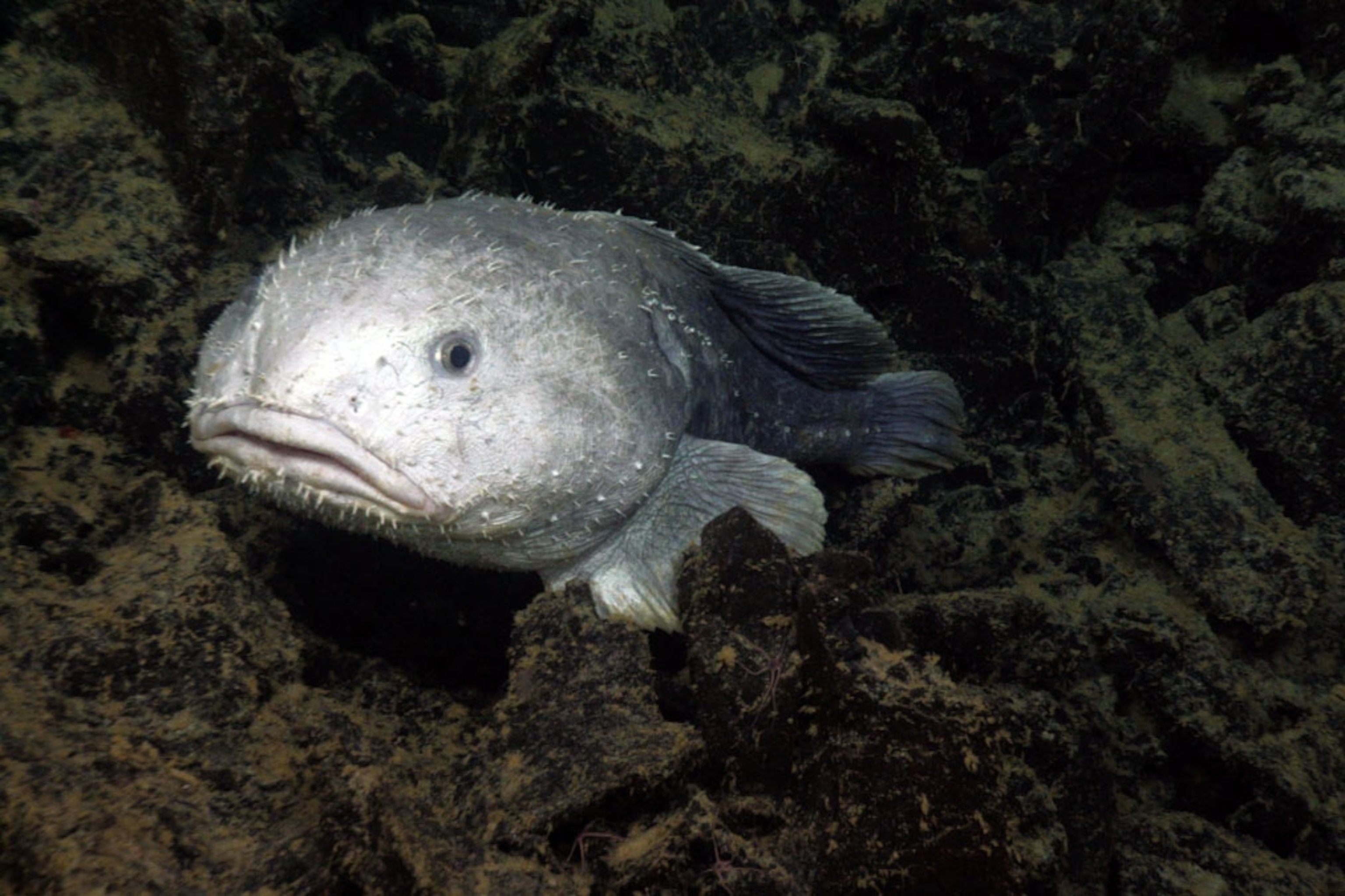

The blobfish is just as harmless and adorable as it looks. It is not a predator in its ecosystem, so it does not hunt other animals. Who could have ever guessed a creature so ferocious and beastly was so passive?
Down in the deep, there is very little light. Therefore it does not actively look for food. It generally eats whatever happens to float in front of its face. Crustaceans, mollusks, and sea urchins make up a majority of its diet.
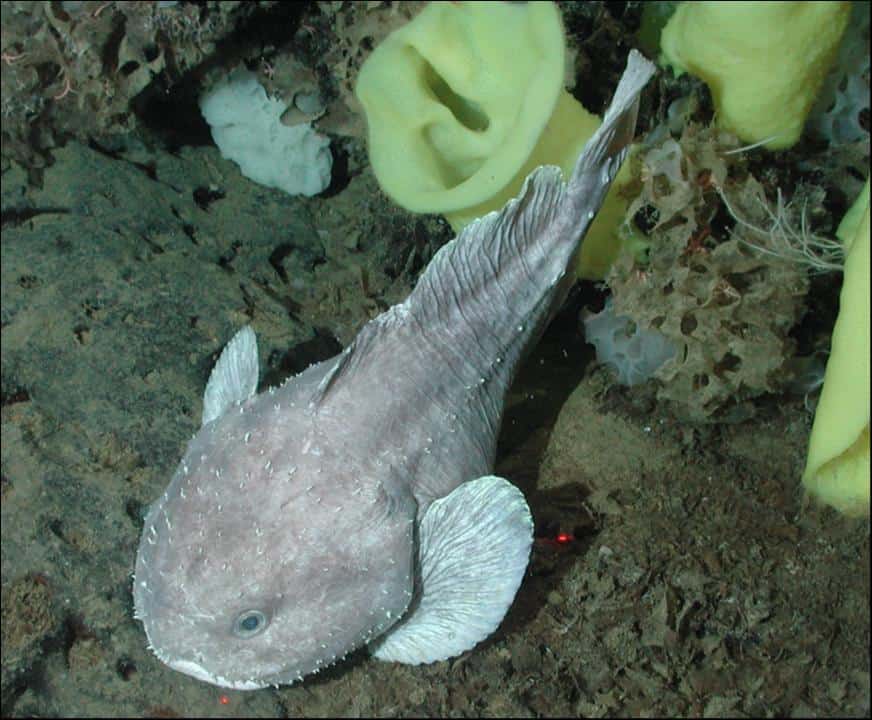

You might be wondering, “Why don’t we eat blobfish?” First of all, they live so deep in the ocean, it would be ridiculous to do the work to catch one just to eat it. The second reason is more somber.
The blobfish is an endangered species. It is estimated that only 420 blobfish remain in the world. This is because even though these fish lay thousands of eggs, only a few survive to adulthood. Additionally, overfishing and deep-sea trawling have resulted in the decline of their population.
As funny as it is to make memes with the blobfish’s goofy-looking face, these creatures could disappear off of the Earth forever if we do not start taking conservation efforts seriously. As a collective, we could work together to protect our oceans and the many unique creatures that inhabit it.