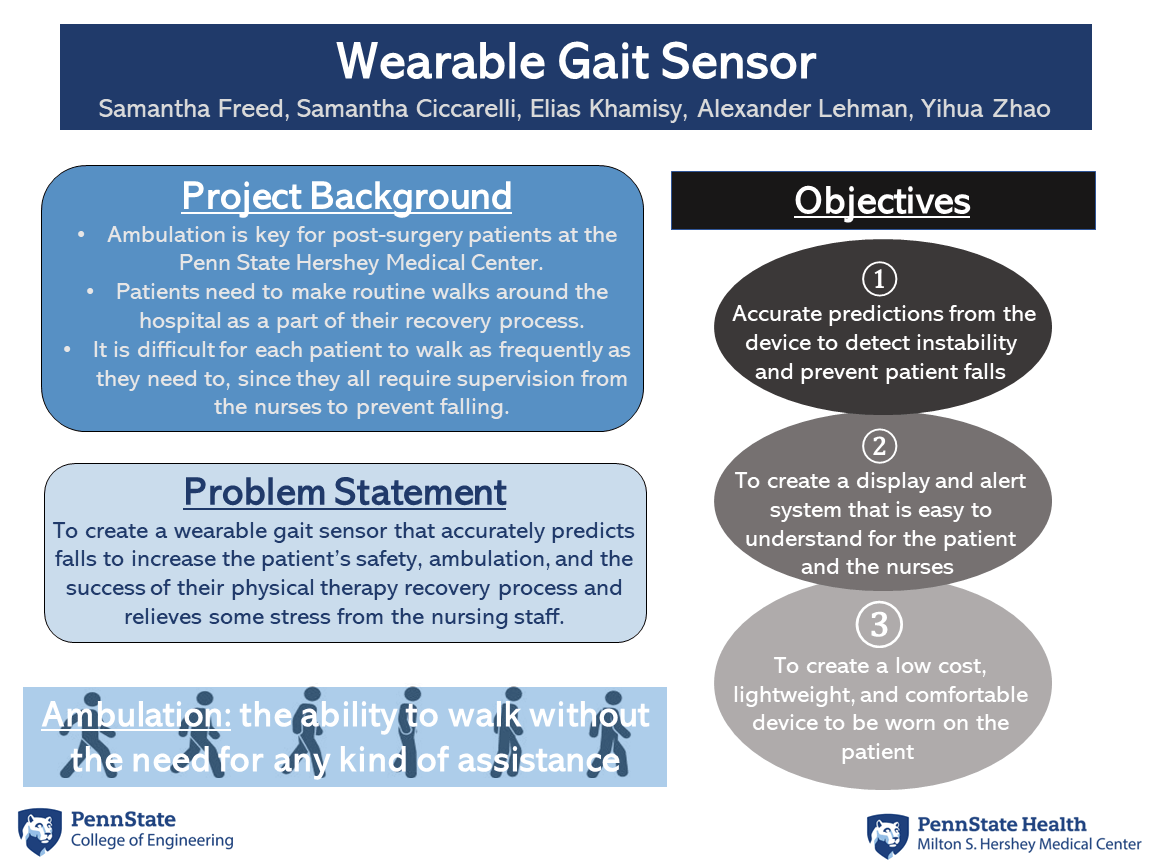
The objective of this project is to create a wearable gait sensor that accurately predicts falls to increase the patient’s safety, ambulation, and the success of their physical therapy recovery process and relieves some stress from the nursing staff.

Sponsored by: Penn State Hershey Medical Center
Team Members
Samantha Freed Samantha Ciccarelli Elias Khamisy Alexander Lehman Yihua Zhao
Instructor: Lyndsey Hylbert
Project Poster
Click on any image to enlarge.
Project Video
Project Summary
Overview
After surgery, patients at the Penn State Hershey Medical Center need to make routine walks around the hospital as a part of their recovery process. Due to the large number of patients and the low number of nurses, it is difficult for each patient to walk as frequently as they need to, since they all require supervision while walking. They need supervision because they are unstable and at a high risk of falling. If they fall that will affect their recovery process and the nurses who were helping them.
The proposed solution to this problem is to create a wearable device for the patients to wear while they are walking. This device will detect the patient’s instability, so if they are at risk of falling, the nurse can respond accordingly. This will give the patients and nurses ease of mind when they take their daily walks. It also gives nurses the opportunity to take more than one patient out at a time for a walk, since the device will alert them when a specific patient needs attention.
Objectives
The goals of the wearable gait sensor include:
-To create a low cost, lightweight, and comfortable device to be worn on the patient
-Accurate predictions from the device to detect instability and prevent patient falls
-To create a display and alert system that is easy to understand for the patient and the nurses
Approach
-The sponsor detailed the idea, needs, and specifications she was interested in for the device.
-The team visited the Penn State Hershey Medical Center to see the patients and the environment the device would be used in.
-Throughout the semester the team had weekly zoom meetings with the sponsor to keep her updated on progress and to get her input on the directions they were going in.
-Concepts for the device were thought up independently by each team member and compared to combine the best parts of each design.
-The ideas were weighed by the team and sponsor to verify the best possible choices.
-The team recognized the need for a recorded baseline for each patient to compare experimental walking data to.
-A phone with gyroscope and accelerometer capabilities was purchased, along with drunk goggles to simulate instability and an armband to hold the phone to the patient.
-Members of the group coded in Python to determine a way to record a baseline, pull data from the baseline, and compare this to the gyroscope and accelerometer data from the phone in real time.
-Tests were run on team members, using the phone and Python code to compare a walking baseline to an unstable walk simulated by spinning and wearing drunk goggles.
-The data was graphed, analyzed, and reported as a percentage of stability for patients and hospital staff to easily understand.
Outcomes
-The device will predict how well the patient is walking for patients of any age or any walking ability.
-Accurate predictions will give the nurses ease of mind when they need to take the patients out.
-Accurate predictions will give the patients more confidence in themselves and their walking ability which will increase their ambulation.
-Increased periods of safe walking will improve the patients’ health and speed up their recovery process.
–>