By now, we all know what a solar cell looks like and does. Simply put, it’s a squarish tile that converts light energy to electrical energy. That’s great and all, but one problem with modern solar cells is that they’re kind of difficult to integrate into buildings and other appliances. A new type of solar cell may get rid of that problem.

Researchers have developed a new type of transparent solar cell. Transparent solar cells have actually been around since 2012 but those were the first model and were extremely inefficient as any new technology would be. Back in 2012, researchers at UCLA created these see-through solar panels that were also lightweight and flexible, almost like plastic. You might be wondering, if solar panels absorb sunlight then how is it possible to make them transparent unless they are extremely inefficient? Well, light from the sun contains more than just visible light; it also contains ultraviolet rays and infrared rays which are invisible to the human eye. Transparent solar cells work by absorbing these forms of the electromagnetic spectrum instead of the traditional visible light rays, making the solar cells transparent.
Since that breakthrough in transparent solar cells, research on the topic has continued. In February of 2013, an MIT start up company began to create a similar product. Their vision was to use the solar panel on electronic displays, such as on cell phones and tablets. However, the technology was still developing and the solar cells created by the start up only had a 2% efficiency rate while being 60% transparent. Their goal is to reach 10% efficiency and they plan to do that by utilizing more of the infrared spectrum. While a 2% efficiency rate is enough to power the lights in your house or a computer (if you replaced all your windows with the solar cells), it’s still no where near the level of efficiency needed to be marketable.

Using a transparent solar cell to (barely) power a digital clock
But now, “windows that double as solar panels could soon be a reality following a breakthrough in quantum dot research that could have significant implications on the way the sun’s energy is harvested in the future.” I’ll admit, I’m not qualified to explain what “quantum dot research” is since I’ve never heard of it before. According to the article, quantum dots are “nanocrystals made of semiconductor materials” which are already widely used in transistors, LEDs, and lasers. Researchers at the Los Alamos National Laboratory and the University of Milano-Bicocca have created a new type of quantum dot that can be embedded into transparent polymers (like glass or plastic) to absorb the sun’s energy. This type of transparent solar cell is different from the previously mentioned solar cells that absorbed energy from the non-visible spectrum of light. This type of solar cell uses something called “large-area luminescent solar concentrators (LSCs)” that take advantage of the new type of quantum dots. Instead of having the transparent solar cell absorb light energy directly, the LCSs “captures” light energy and transports it through the quantum dots to solar cells at the edge of the transparent material.
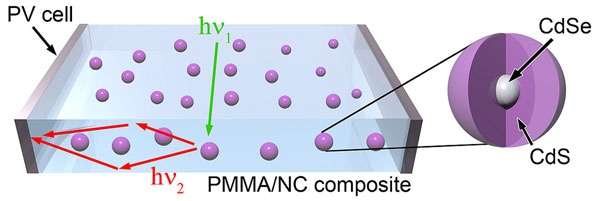
So essentially, this isn’t a new type of solar cell, it’s just a new way of redirecting and focusing the light energy onto the solar cells. “Sunlight captured is radiated through the LSC towards a small solar cell on the slab’s edge, which increases power efficiency in a way that could have broad applications in future solar cells.”
If this kind of technology becomes available to the public in the future, it can be used to make many interesting new concepts. Going back to the introduction, solar cells like these would be so much easier to integrate into buildings. For example, imagine replacing all of the windows in your house with transparent solar cells, or even all of the windows on a skyscraper with solar cells. As you can see, this would greatly decrease our reliance on non-renewable energy resources. Transparent solar cells can be utilized in other ways than on buildings, too. Imagine an electric car that has solar cells as windows or even a cell phone or table that doesn’t need to be charged since the screen is a solar cell. The possibilities with this new technology are endless.
http://www.ibtimes.co.uk/solar-panel-windows-made-possible-by-quantum-dot-breakthrough-1445213
http://www.pv-magazine.com/news/details/beitrag/ucla-develops-transparent-solar-cell_100007824/
http://www.extremetech.com/extreme/149163-mit-startup-makes-transparent-solar-cells-that-will-allow-your-smartphone-to-power-itself