When we hear people discussing politics, often times it is common to hears world like “capitalism” and “communism” being thrown around as if they are things we see on a daily basis. In reality no government around the world holds a true capitalist or communist economy, rather they each fall somewhere along the spectrum in between the two extremes. Due to the common misconceptions around the concepts, and being an Econ major myself—highly interest in the topic— I wanted to take some time to explore the definitions, pros, and cons, of the two systems.

The formal definition of capitalism is “an economic system in which a country’s businesses and industry are controlled and run for profit by private owners rather than by the government” The general idea here, is that the people who produce the best products will be the ones who are successful and will eventually become wealthy. This form of economy tends to promote hard-work, innovation, and completion amongst members of society. We also here terms such as “Laissez-faire” or “free market” being associated with capitalism, which essentially means there is a limited amount of government intervention in the economy— with it really only stepping in to prevent the formation of monopolies and unfair trade. In a pure free market, things like tariffs and subsidies do not exist, and everything bends according to the laws of supply and demand. The downfalls here are that those who do not have competitive skills, such as the poor, elderly, and disabled, do not have the same abilities to produce in a market as others do, and are often not taken well care of in this type of system. The United States generally tends to lean closer to this side of the capitalism vs. communism spectrum.
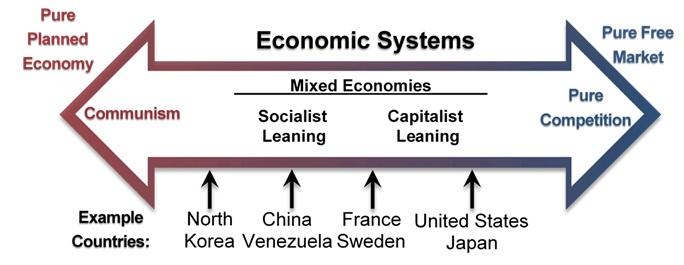
On the other hand, the formal definition of communism is “a political movement that believes in an economic system in which the state controls the means of producing everything for the people. It aims to create a society in which everyone is treated equally” This idea was popularized by Karl Marx, an economist who believed each person should do what they are good at and what makes them happy, and the total production of this across society will be split evenly. One of the biggest strengths of this type of economy is that due to the government having so much control, large productions are able to be executed quickly. However the disadvantages are that because the government controls price, instead of the lows of supply and demand, it is easy for products to be come out of date with consumer preferences. It is also not a strong system to promote competition and hard-work as people lack the incentive for these things if everyone is ultimately treated the same in the end.
Overall, both economies have major pros and cons, but it is best to remember that it is rare to see a country entirely follow one system or the other. (sources.)