This article discussed about a framework and guidelines for Architecture Governance.
Levels of Governance within the Enterprise
Architecture Governance is the practice and orientation by which Enterprise Architectures and other architectures are managed and controlled at an enterprise-wide level.
Architecture Governance typically does not operate in isolation, but within a hierarchy of governance structures, which, particularly in the larger enterprise, can include all of the following as distinct domains with their own disciplines and processes:
- Corporate Governance
- Technology Governance
- IT Governance
- Architecture Governance
Each of these domains of governance may exist at multiple geographic levels – global, regional, and local – within the overall enterprise.
Corporate governance is thus a broad topic, beyond the scope of an Enterprise Architecture framework such as the TOGAF framework.
This and related subsections are focused on Architecture Governance; but they describe it in the context of enterprise-wide governance, because of the hierarchy of governance structures within which it typically operates, as explained above.
In particular, this and following sections aim to:
- Provide an overview of the nature of governance as a discipline in its own right
- Describe the governance context in which Architecture Governance typically functions within the enterprise
- Describe an Architecture Governance Framework that can be adapted and applied in practice, both for Enterprise Architecture and for other forms of IT architecture
Nature of Governance
Governance: A Generic Perspective
Governance is essentially about ensuring that business is conducted properly. It is less about overt control and strict adherence to rules, and more about guidance and effective and equitable usage of resources to ensure sustainability of an organization’s strategic objectives.
The following outlines the basic principles of corporate governance, as identified by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD):
- Focuses on the rights, roles, and equitable treatment of shareholders
- Disclosure and transparency and the responsibilities of the board
- Ensures:
- Sound strategic guidance of the organization
- Effective monitoring of management by the board
- Board accountability for the company and to the shareholders
- Board’s responsibilities:
- Reviewing and guiding corporate strategy
- Setting and monitoring achievement of management’s performance objectives
Supporting this, the OECD considers a traditional view of governance as: “… the system by which business corporations are directed and controlled. The corporate governance structure specifies the distribution of rights and responsibilities among different participants in the corporation – such as the board, managers, shareholders, and other stakeholders – and spells out the rules and procedures for making decisions on corporate affairs. By doing this, it also provides the structure through which the company objectives are set, and the means of attaining those objectives and monitoring performance” (Source: OECD, 2001).
Characteristics of Governance
The following characteristics have been adapted from Corporate Governance (Naidoo, 2002) and are positioned here to highlight both the value and necessity for governance as an approach to be adopted within organizations and their dealings with all involved parties:
- Discipline
- All involved parties will have a commitment to adhere to procedures, processes, and authority structures established by the organization.
- Transparency
- All actions implemented and their decision support will be available for inspection by authorized organization and provider parties.
- Independence
- All processes, decision-making, and mechanisms used will be established so as to minimize or avoid potential conflicts of interest.
- Accountability
- Identifiable groups within the organization – e.g., governance boards who take actions or make decisions – are authorized and accountable for their actions.
- Responsibility
- Each contracted party is required to act responsibly to the organization and its stakeholders.
- Fairness
- All decisions taken, processes used, and their implementation will not be allowed to create unfair advantage to any one particular party.
Technology Governance
Technology governance controls how an organization utilizes technology in the research, development, and production of its goods and services. Although it may include IT governance activities, it often has broader scope.
Technology governance is a key capability, requirement, and resource for most organizations because of the pervasiveness of technology across the organizational spectrum.
Recent studies have shown that many organizations have a balance in favor of intangibles rather than tangibles that require management. Given that most of these intangibles are informational and digital assets, it is evident that businesses are becoming more reliant on IT: and the governance of IT – IT governance – is therefore becoming an even more important part of technology governance.
These trends also highlight the dependencies of businesses on not only the information itself but also the processes, systems, and structures that create, deliver, and consume it. As the shift to increasing value through intangibles increases in many industry sectors, so risk management must be considered as key to understanding and moderating new challenges, threats, and opportunities.
Not only are organizations increasingly dependent on IT for their operations and profitability, but also their reputation, brand, and ultimately their values are also dependent on that same information and the supporting technology.
IT Governance
IT governance provides the framework and structure that links IT resources and information to enterprise goals and strategies. Furthermore, IT governance institutionalizes best practices for planning, acquiring, implementing, and monitoring IT performance, to ensure that the enterprise’s IT assets support its business objectives.
In recent years, IT governance has become integral to the effective governance of the modern enterprise. Businesses are increasingly dependent on IT to support critical business functions and processes; and to successfully gain competitive advantage, businesses need to manage effectively the complex technology that is pervasive throughout the organization, in order to respond quickly and safely to business needs.
In addition, regulatory environments around the world are increasingly mandating stricter enterprise control over information, driven by increasing reports of information system disasters and electronic fraud. The management of IT-related risk is now widely accepted as a key part of enterprise governance.
It follows that an IT governance strategy, and an appropriate organization for implementing the strategy, must be established with the backing of top management, clarifying who owns the enterprise’s IT resources, and, in particular, who has ultimate responsibility for their enterprise-wide integration.
An IT Controls Framework – COBIT
As with corporate governance, IT governance is a broad topic, beyond the scope of an Enterprise Architecture framework such as the TOGAF framework. A good source of detailed information on IT governance is the COBIT framework (Control OBjectives for Information and related Technology). This is an open standard for control over IT, developed and promoted by the IT Governance Institute (ITGI), and published by the Information Systems Audit and Control Foundation (ISACF). COBIT controls may provide useful aides to running a compliance strategy.
Architecture Governance: Overview
Architecture Governance Characteristics
Architecture Governance is the practice and orientation by which Enterprise Architectures and other architectures are managed and controlled at an enterprise-wide level. It includes the following:
- Implementing a system of controls over the creation and monitoring of all architectural components and activities, to ensure the effective introduction, implementation, and evolution of architectures within the organization
- Implementing a system to ensure compliance with internal and external standards and regulatory obligations
- Establishing processes that support effective management of the above processes within agreed parameters
- Developing practices that ensure accountability to a clearly identified stakeholder community, both inside and outside the organization
Architecture Governance as a Board-Level Responsibility
As mentioned above, IT governance has recently become a board responsibility as part of overall business governance. The governance of an organization’s architectures is a key factor in effective IT/business linkage, and is therefore increasingly becoming a key board-level responsibility in its own right.
This section aims to provide the impetus for opening up IT and Architecture Governance so that the business responsibilities associated with architecture activities and artifacts can be elucidated and managed.
The TOGAF Standard and Architecture Governance
Phase G of the TOGAF ADM is dedicated to implementation governance, which concerns itself with the realization of the architecture through change projects. Implementation governance is just one aspect of Architecture Governance, which covers the management and control of all aspects of the development and evolution of Enterprise Architectures and other architectures within the enterprise.
Architecture Governance needs to be supported by an Architecture Governance Framework which assists in identifying effective processes so that the business responsibilities associated with Architecture Governance can be elucidated, communicated, and managed effectively.
Architecture Governance Framework
This section describes a conceptual and organizational framework for Architecture Governance
As previously explained, Phase G of the TOGAF ADM is dedicated to implementation governance, which concerns itself with the realization of the architecture through change projects.
Implementation governance is just one aspect of Architecture Governance, which covers the management and control of all aspects of the development and evolution of Enterprise Architectures and other architectures within the enterprise.
Architecture Governance needs to be supported by an Architecture Governance Framework, described below. The governance framework described is a generic framework that can be adapted to the existing governance environment of an enterprise. It is intended to assist in identifying effective processes and organizational structures, so that the business responsibilities associated with Architecture Governance can be elucidated, communicated, and managed effectively.
Architecture Governance Framework – Conceptual Structure
Key Concepts
Conceptually, Architecture Governance is an approach, a series of processes, a cultural orientation, and set of owned responsibilities that ensure the integrity and effectiveness of the organization’s architectures.
The key concepts are illustrated in Figure 44-1 .
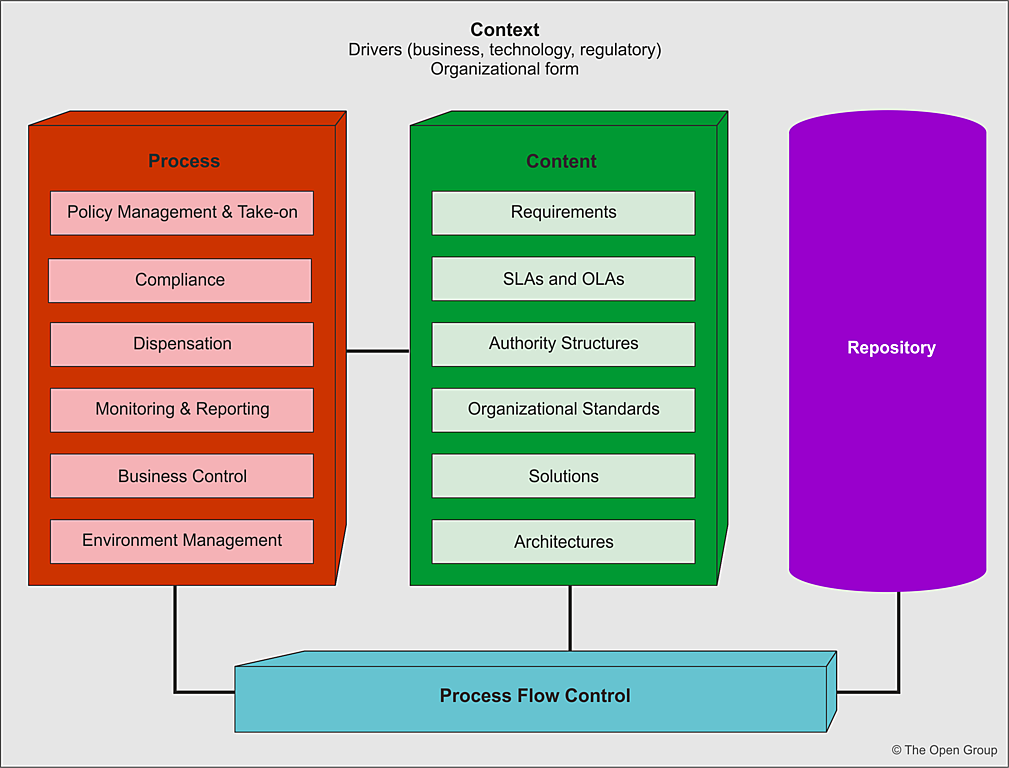
The Architecture Governance Framework is integral to the Enterprise Continuum, and manages all content relevant both to the architecture itself and to Architecture Governance processes.
Key Architecture Governance Processes
Governance processes are required to identify, manage, audit, and disseminate all information related to architecture management, contracts, and implementation. These governance processes will be used to ensure that all architecture artifacts and contracts, principles, and Operational-Level Agreements (OLAs) are monitored on an ongoing basis with clear auditability of all decisions made.
Policy Management and Take-On
All architecture amendments, contracts, and supporting information must come under governance through a formal process in order to register, validate, ratify, manage, and publish new or updated content. These processes will ensure the orderly integration with existing governance content such that all relevant parties, documents, contracts, and supporting information are managed and audited.
Compliance
Compliance assessments against Service-Level Agreements (SLAs), OLAs, standards, and regulatory requirements will be implemented on an ongoing basis to ensure stability, conformance, and performance monitoring. These assessments will be reviewed and either accepted or rejected depending on the criteria defined within the governance framework.
Dispensation
A Compliance Assessment can be rejected where the subject area (design, operational, service level, or technology) are not compliant. In this case the subject area can:
- Be adjusted or realigned in order to meet the compliance requirements
- Request a dispensation
Where a Compliance Assessment is rejected, an alternate route to meeting interim conformance is provided through dispensations. These are granted for a given time period and set of identified service and operational criteria that must be enforced during the lifespan of the dispensation. Dispensations are not granted indefinitely, but are used as a mechanism to ensure that service levels and operational levels are met while providing a level of flexibility in their implementation and timing. The time-bound nature of dispensations ensures that they are a major trigger in the compliance cycle.
Monitoring and Reporting
Performance management is required to ensure that both the operational and service elements are managed against an agreed set of criteria. This will include monitoring against SLAs and OLAs, feedback for adjustment, and reporting.
Internal management information will be considered in Environment Management .
Business Control
Business Control relates to the processes invoked to ensure compliance with the organization’s business policies.
Environment Management
This identifies all the services required to ensure that the repository-based environment underpinning the governance framework is effective and efficient. This includes the physical and logical repository management, access, communication, training, and accreditation of all users.
All architecture artifacts, service agreements, contracts, and supporting information must come under governance through a formal process in order to register, validate, ratify, manage, and publish new or updated content. These processes will ensure the orderly integration with existing governance content such that all relevant parties, documents, contracts, and supporting information are managed and audited.
The governance environment will have a number of administrative processes defined in order to effect a managed service and process environment. These processes will include user management, internal SLAs (defined in order to control its own processes), and management information reporting.
Architecture Governance Framework – Organizational Structure
Overview
Architecture Governance is the practice and orientation by which Enterprise Architectures and other architectures are managed and controlled. In order to ensure that this control is effective within the organization, it is necessary to have the correct organizational structures established to support all governance activities.
An Architecture Governance structure for effectively implementing the approach described in this section will typically include the following levels, which may in practice involve a combination of existing IT governance processes, organizational structures, and capabilities. They will typically include the following:
- Global governance board
- Local governance board
- Design authorities
- Working parties
The architecture organization illustrated in Figure 44-2 highlights the major structural elements required for an Architecture Governance initiative. While each enterprise will have differing requirements, it is expected that the basics of the organizational design shown in Figure 44-2 will be applicable and implementable in a wide variety of organizational types.

Key Areas
Figure 44-2 identifies three key areas of architecture management: Develop, Implement, and Deploy. Each of these is the responsibility of one or more groups within the organization, while the Enterprise Continuum is shown to support all activities and artifacts associated with the governance of the architectures throughout their lifecycle.
The Develop responsibilities, processes, and structures are usually linked to the TOGAF ADM and its usage, while the Implement responsibilities, processes, and structures are typically linked to Phase G.
As mentioned above, the Architecture Governance Framework is integral to the Enterprise Continuum, and manages all content relevant both to the architectures themselves and to Architecture Governance processes.
Operational Benefits
As illustrated in Figure 44-2 , the governance of the organization’s architectures provides not only direct control and guidance of their development and implementation, but also extends into the operations of the implemented architectures.
The following benefits have been found to be derived through the continuing governance of architectures:
- Links IT processes, resources, and information to organizational strategies and objectives
- Integrates and institutionalizes IT best practices
- Aligns with industry frameworks such as COBIT (planning and organizing, acquiring and implementing, delivering and supporting, and monitoring IT performance)
- Enables the organization to take full advantage of its information, infrastructure, and hardware and software assets
- Protects the underlying digital assets of the organization
- Supports regulatory and best practice requirements such as auditability, security, responsibility, and accountability
- Promotes visible risk management
These benefits position the TOGAF Architecture Governance Framework as an approach, a series of processes, a cultural orientation, and a set of owned responsibilities, that together ensure the integrity and effectiveness of the organization’s architectures.
Architecture Governance in Practice
This section provides practical guidelines for the effective implementation of Architecture Governance
Architecture Governance – Key Success Factors
It is important to consider the following to ensure a successful approach to Architecture Governance, and to the effective management of the Architecture Contract:
- Best practices for the submission, adoption, re-use, reporting, and retirement of architecture policies, procedures, roles, skills, organizational structures, and support services
- Organizational responsibilities and structures to support the Architecture Governance processes and reporting requirements
- Integration of tools and processes to facilitate the take-up of the processes, both procedurally and culturally
- Criteria for the control of the Architecture Governance processes, dispensations, compliance assessments, SLAs, and OLAs
- Internal and external requirements for the effectiveness, efficiency, confidentiality, integrity, availability, compliance, and reliability of all Architecture Governance-related information, services, and processes
Elements of an Effective Architecture Governance Strategy
Architecture Governance and Corporate Politics
An Enterprise Architecture imposed without appropriate political backing is bound to fail. In order to succeed, the Enterprise Architecture must reflect the needs of the organization. Enterprise Architects, if they are not involved in the development of business strategy, must at least have a fundamental understanding of it and of the prevailing business issues facing the organization. It may even be necessary for them to be involved in the system deployment process and to ultimately own the investment and product selection decisions arising from the implementation of the Technology Architecture.
There are three important elements of Architecture Governance strategy that relate particularly to the acceptance and success of architecture within the enterprise. While relevant and applicable in their own right apart from their role in governance, and therefore described separately, they also form an integral part of any effective Architecture Governance strategy.
- A cross-organizational Architecture Board must be established with the backing of top management to oversee the implementation of the Enterprise Architecture Governance strategy
- A comprehensive set of Architecture Principles should be established, to guide, inform, and support the way in which an organization sets about fulfilling its mission through the use of IT
- An Architecture Compliance strategy should be adopted – specific measures (more than just a statement of policy) to ensure compliance with the architecture, including Project Impact Assessments, a formal Architecture Compliance review process, and possibly including the involvement of the architecture team in product procurement
Referenced Article:
The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 – Architecture Governance. https://pubs.opengroup.org/architecture/togaf9-doc/arch/chap44.html. Accessed 7 June 2023.