Nanofibers are an ideal support material for enzyme immobilization and biocatalytic engineering due to their high surface-to-mass ratios. Non-woven, entangled nanofiber mats can easily be retrieved from the reaction media and recycled, allowing easy separation and recovery of the enzyme. In these developments, the most challenging problem is how to maintain the enzyme activity over an extended period of time. In collaboration with Dr. Jungbae Kim at Korea University, we have developed unique and efficient ways of anchoring and stabilizing enzymes on nanofiber surfaces and dispersing hydrophobic nanofibers in aqueous solutions.∗

Application of the electro-spinning technique, a most widely used method for production of polymeric nanofibers, to hydrogels and conducting polymers has been difficult since these materials cannot be dissolved in solution for electro-spinning. Our group developed “reactive electro-spinning” processes to fabricate functional nanofibers of hydrogels and conducting polymers.∗∗ We are currently investigating enzyme immobilization and stabilization on these nanofibers for biocatalysis and biosensing applications.
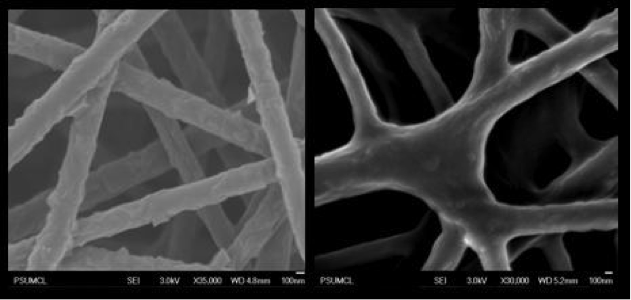
- ∗ B. C. Kim, X. Zhao, H.-K. Ahn, J. H. Kim, H.-J. Lee, K. W. Kim, S. Nair, E. Hsiao, H. Jia, M.-K. Oh, B. I. Sang, B.-S. Kim, S. H. Kim, Y. Kwon, S. Ha, M. B. Gu, P. Wang, J. Kim “Highly stable enzyme precipitate coatings and their electrochemical applications” Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1980–1986;
- ∗S. Nair, J. Kim, B. Crawford, and S. H. Kim, “Improving Biocatalytic Activity of Enzyme-Loaded Nanofibers by Dispersing Entangled Nanofiber Structure” Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1266-1270.
- ∗∗ S. Nair, E. Hsaio, and S. H. Kim “Melt-Welding and Improved Electrical Conductivity of Nonwoven Porous Nanofiber Mats of Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Grown on Electrospun Polystyrene Fiber Template” Chem. Mater., 2009, 21, 115-121.