Post World War I Russia saw Joseph Stalin’s rise to power and Marxism-Leninism as a significant communist ideology. Marxism-Leninism was ultimately Vladimir Lenin’s interpretation of Karl Marx’s ideologies (Raico). Marxism-Leninism is the political ideology of the Stalinist and Maoist political parties and is still present in China, Cuba, Laos, and Vietnam. Under Marxism-Leninism the goal is to move from a capitalist state to a communist usually through a revolution. For a period, the state controls the economy and production, with the intention of pursuing a classless and stateless society.
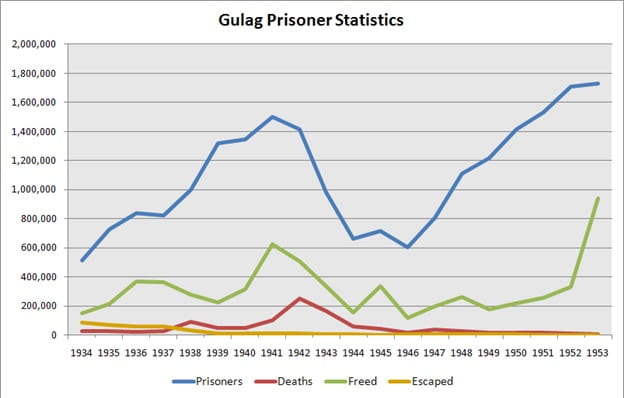
While communism sounds great, and the will of the people. That wasn’t reality in the USSR. Lenin & Stalin would issue in strong political coercion. Everything from forced labor, to executions help mold the communist society. Forced labor camps were known as Gulags where anti-Stalinists were forced into labor and worked to death. As the Gulag system advanced and became more rampant Stalin would move from imprisoning opposing political faction members to educated members of society. Doctors, writers, intellects, students, artists and scientists. Historians estimate the ten percent of political prisoners were killed in Gulags. Unlike Holocaust camps, the atrocities of Gulag would not become known to the world until 1991 after the fall of the Soviet Union (History.com).
After World War II Communism as an ideology was spread through Western Europe due to the Russia’s large territory and its army occupying much of western Europe. This would eventually result in the Union Soviet Socialist Republics. These countries included Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Bulgaria, and Romania. Their relationship with Russia would last for over 50 years with their cultural values lining up very closely with communism (The Pennsylvania State University).
Communism is generally thought of as a left-wing political ideology and has strong opposition to fascism as seen in Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, or what some consider Trumpism in the United States. Communists often oppose capitalism and imperialism.
References:
Raico, R. (2020, April 03). Marxist Dreams and Soviet Realities. Retrieved November 19, 2020, from https://www.cato.org/publications/commentary/marxist-dreams-soviet-realities
History.com Editors. (2018, March 23). Gulag. Retrieved November 19, 2020, from https://www.history.com/topics/russia/gulag
The Pennsylvania State University (n.d.). Lesson 13: Eastern Europe and Russia. Retrieved November 19, 2020, from https://psu.instructure.com/courses/2075490/modules/items/29697221
