
What if told you that there was a plant on this plant that had some of the strongest naturally accruing fibers and can be made into thousands of different products including clothes, food, plastics, fuel, and even building materials? Before going any further in this blog post it is important to delineate the difference between industrial hemp and recreational and medical marijuana. Medical and recreational marijuana has a chemical in it called delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol or THC for short; this is the chemical in marijuana that gets high. While hemp is part of the cannabis family and looks almost exactly like regular marijuana, it is extremely different. Industrial hemp that is used to make a variety of products has little to no THC in it. In fact in America in order to make products out of hemp there has to be less than .03% THC in it (HempBasic.com). Average weed is 3 to 7% THC with the highest percentages being at around 30%. What this means is that you could smoke an entire field of hemp and you would not get high in the slightest. It is for the reason the hemp cannot get you high because it’s lacking of THC that it should not be thrown in with the highly debatable and social topic of recreational and medical marijuana. The legality of Hemp in the United States and across the world is quite complicated because of similarities to THC potent marijuana so I will not be getting into that part of it. I will instead focus on all of the vast industrial uses of hemp. I often feel that in the hot topic of marijuana hemp gets left out and not enough people are aware of its amazing capabilities and potential.
Lets first begin with how hemp matches up to another well known fiber, cotton. According to hempbasics.com compared to cotton “1 acre of hemp will produce as much fiber as 2 to 3 acres of cotton. Hemp fiber is stronger and softer than cotton, lasts twice as long as cotton, and will not mildew” (HempBasic.com). Not only that but the climate in which hemp grows in is much more versatile then cotton, requires less water and unlike cotton requires no pesticides or herbicides (HempBasic.com). What that means that as far as growing hemp goes it is much more environmentally friendly then cotton because harmful chemicals are not needed in the growing process and it require less water. Here is a great diagram from weebly.com that shows some of the differences and benefits of hemp over cotton.
There are literally thousands of items that can be made out of hemp like clothes, paper, food, and much more. I am going to focus however on three different things that can be made out of hemp that I find to be not only the most interesting but the most important. These three items are plastics, fuel, and building materials. These three items alone prove how valuable of material hemp is and why its cultivation should extremely widespread.
Here is a diagram that helps to give you more of sense of things hemp can be made into:
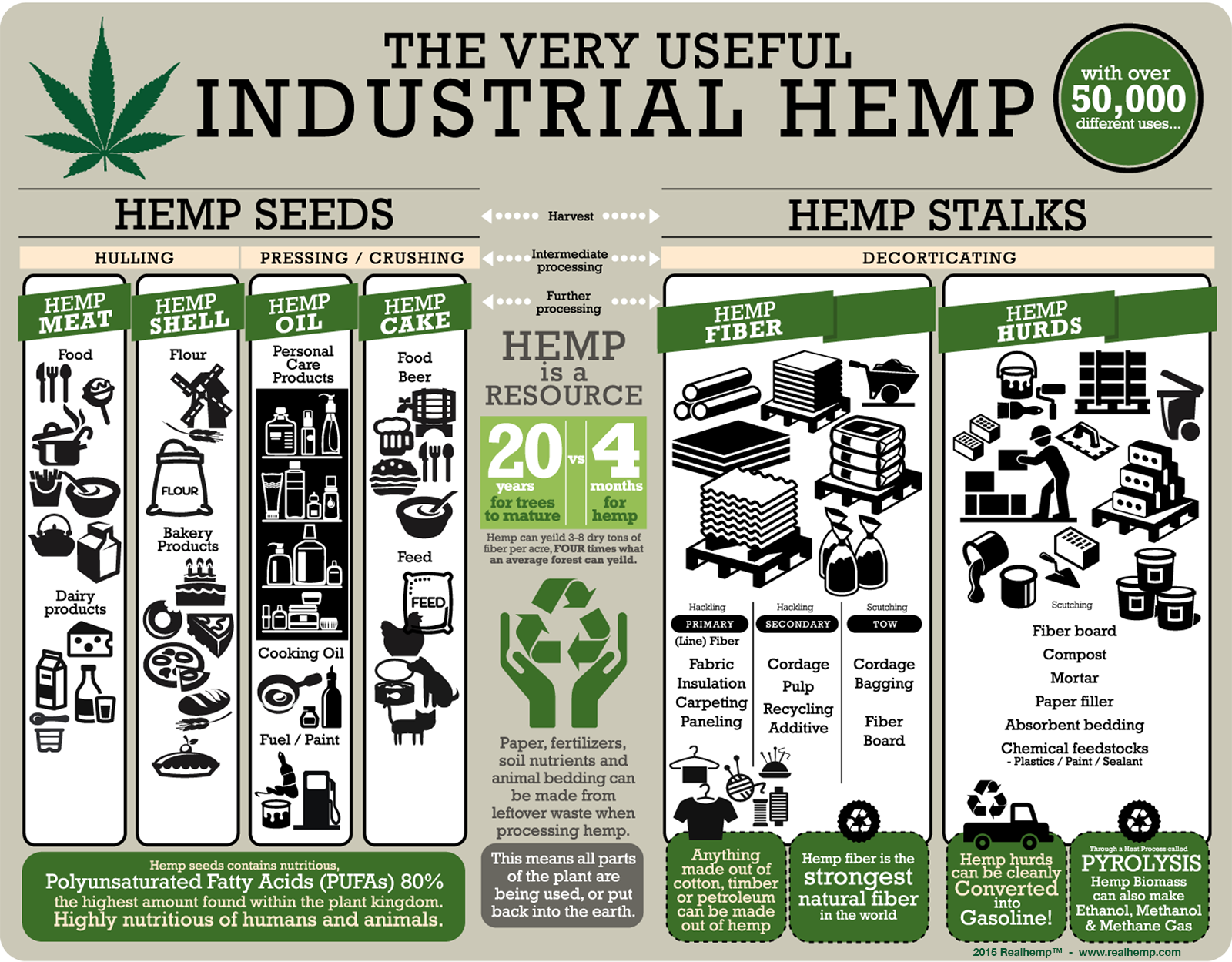
As far as plastics go, there is a common chemical in that used in the process of making most plastics. Plastics like rayon, and cellophane, are made with something that is called cellulose. Cellulose is what makes up plants cell walls, and it can be extracted from plants to make these types of plastic. Hemp contains around 65 to 70% cellulose, which can be extracted and made into plastics (SensiSeeds.com). To put this in comparison to other plants have high cellulose content flax has about 65 to 75%, wood has 40%, and cotton can have up to 90% (SensiSeeds.com). That means that hemp is almost as good as cotton for making plastics, but like I said earlier is more environmentally friendly to grow and has many more benefits. Once plastics are made out of hemp they can then turned into items like DVD cases, shower lining, and even car parts (TreeHuger.com).
Another item that can be made out of hemp is fuel. Just like vegetable oil you can make biofuel out of hemp. By turning hemp into hemp oil it can be used to create biodiesel (TreeHuger.com). Basically what biodiesel is clean and renewable fuel that does not negatively impact the environment when it is burned (BioDiesel.org). Biodiesel is made through a process called “transesterification whereby the glycerin is separated from the fat in a plant. The process leaves behind two products, methyl esters (the chemical name for biodiesel) and glycerin” (BioDiesel.org). Biofuel is extremely important when comes to talking about the future of renewable energies, it’s just one potential way to replace the harmful and nonrenewable gasoline that is used in cars. According to treehuger.com hemp could also be “utilized to make liquid fuels that are chemically identical to petroleum-based gasoline or diesel as well” (TreeHuger.com). The use of hemp for fuel is not only possible but could be a great clean and renewable resource to help fuel the country.
Finally we come to one of the most impressive uses of hemp, that being building materials. Hemp can be made into insulation that is more environmentally friendly as well as a better form of wood and concrete. When you take the fibers of hemp and make them into boards they are stronger and more flexible then wood while being fire and root resistant (TreeHuger.com). These boards can then be taken and made it houses that are must strong and more resistant to extreme conditions then regular houses. Hemp can also be taken and made into an even strong form that is dubbed “hempcrete”. Not only is this hempcrete “stronger and lighter then concrete” (TreeHuger.com), but it is “fireproof and waterproof” (HempBasic.com). According to hemp basics hempcrete is created by “The silica leached from the soil by the plant combined with unslaked lime forms a chemical bond similar to cement” (HempBasic.com). This has a massive impact on the building industry, not only because these hemp products are stronger, more resistant, and better then their counterparts but because they are also environmentally friendly.
So far when talking about hemp, its capabilities to be incredibly environmentally friendly have been a recurring topic when discussing hemp. However the previously mentioned points are not the full extent of hemps abilities to help save our planets ecosystems. By far hemps most important contribution to not only science but the world is its ability to slow and even potentially stop deforestation. Deforestation is an incredibly serious and important topic because it not only destroys the trees we need for oxygen but kills a lot of biodiversity on our planet that is so unique and precious (Weebly.com). According to weebly.com when compared to trees hemp can “produces 4 times the raw material than trees for paper making. Hemp can be planted between 1-3 times a season, depending on location and can be recycled up to 10 times, compared to 3 or 4 for wood pulp paper” (Weebly.com) . Why this is important to deforestation is that hemp can do almost the exact same things as trees like make homes, paper, and other materials but much more renewably and easily. Hemp works just as good as wood and causes way less damage to the environment to produce. It is for those reasons that hemp can help fight the epidemic of deforestation.
Overall hemp is an extremely versatile fiber that has thousand of incredible industrial uses. Unfortunately due to its similarities to THC filled marijuana it is not as widely used as it should be. I think as recreational and medical marijuana becomes increasingly more legal, the unjust and wrong viewpoints of hemp will change and it will become increasingly available and used in the industrial market. Hemp need to be grown and used more frequently not just for all of its uses but mainly because it’s massive environmental impact. Hemp latterly has the power to help stop deforestation and create a cleaner more renewable future.
Here are my sources:
Picture at the top:http://www.nationofchange.org/sites/default/files/HempPassestoHelpFightRadiation021414.jpg
Hemp diagram 1: http://hempethics.weebly.com/what-is-industrial-hemp.html
Hemp diagram 2: https://www.realhemp.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/hemp-chart-2b.png
http://biodiesel.org/what-is-biodiesel/biodiesel-basics
http://sensiseeds.com/en/blog/hemp-plastics-made/
http://hempethics.weebly.com/what-is-industrial-hemp.html
http://www.treehugger.com/environmental-policy/perfect-plant-7-great-uses-for-industrial-hemp.html

