If you haven’t gotten in an argument with your friends at some point in your life about righties versus lefties then shame on you. Everyone (probably not everybody, just an exaggeration) has had this debate in their life at some point. Whether it is about who are the better athletes or who lives longer, it was a common debate in our lives growing up that has been around for some time. The big claim is that left handed people live shorter lives than right handed people. This is quite a significant statement and got me thinking: is this actually true?
Our world is dominated by right handed people, where just about 10 percent of the world’s population is lefties. Back when this was a bigger debate, roughly around the 90s, not many tools and other resources were made for lefties. Today we see that there are certain desks in schools designed for lefties and special kitchen tools specifically for lefties that was not common back then. The lack of tools for lefties was considered a factor that played into their premature deaths according to BBC News. But this simply just didn’t make sense. Like McManus, a professor of psychology and medical education at University College London and author of Right Hand, Left Hand, said “it’s not at all plausible.” Since this was not true, people had no idea why lefties might have shorter lifespans than righties. This led to experiments.
Null Hypothesis: Lefties do not have shorter lives than righties
Alternative Hypothesis: Lefties do have shorter lives than righties
The most common research on the subject was made by Dr. Diane F. Halpern of California State University and Dr. Stanley Coren of the University of British Columbia. They looked at roughly 1000 cases of people who passed away and found the differences to be “striking.” The researchers found that on average right handed people lived to 75 years of age and left handed people lived to 66 years of age and this trend was apparent in both men and women. They also found that lefties were more than 5 times as likely to die in accidents, mainly driving, than righties. The reason they said was because that the world was not made for lefties. So we go back to this idea that it seems like left handed people just do not belong, or at least at the time, did not belong in society. This is outstandingly interesting to think about how the world was so dominated and by and made for rightes. However, Chris McManus (the same guy mentioned in the previous paragraph) says that Halpern and Coren made a “very subtle error.” He goes on to say that “their mistake was they only looked at the dead..” Because left handed people were becoming more popular as time went on, people started to switch to using their right hands. Society didn’t accommodate for lefties so people may have been born left handed, but then switched later in their lives which would skew the results that Halpern and Coren find. McManus goes on to describe an exaggerated scenario and basically says that lefties living shorter lives than righties is a myth. To read more about that click here.
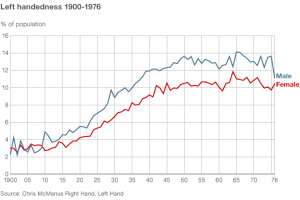
Here is a graph showing how many more lefties there have been over time. From McManus’ publication “Right Hand, Left Hand”
Conclusion
Based on the research I did, it is hard reject the null hypothesis of lefties living shorter lives than righties. From a statistics standpoint, it looks very convincing that lefties do live shorter lives. However, it is just a small sample size and there are other variables that play into this experiment. The research that Coren and Halpern conducted could also suffer from the “file drawer problem” where negative results are not published. Chris McManus made some very convincing points as well about their results being skewed and I agree with him that it could be a myth. I think 20 to 30 years ago, it made more sense to say that lefties lived shorter lives than righties and there were statistics to prove that. Today, our society has adapted to left handed people as they are becoming more popular and I think it is just a myth that they live shorter lives. An argument can be made for both ways so, what do you guys think?
Here are some fun facts I found about lefties that differ from righties that are very interesting.














