Have you ever drove past a huge field or open area and saw very tall objects that look like a pinwheel? Those are called wind turbines and they are used as an alternative source of electricity. They are used to create “clean electricity” which essentially means that no greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere. There are many benefits to wind turbine energy such as no air pollution, sustainability, and cost efficiency.

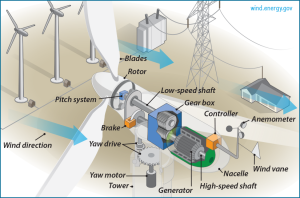
Wind turbines convert mechanical energy from the wind into electrical power. Think of how a wind turbine works as the opposite of how a fan works. A fan uses electricity to make wind, while a wind turbine uses wind to make electricity. They have three main parts: the tower, the blades, and the nacelle. The tower is the long post that connects to the ground. The blades connect to a central hub, called the rotator, that allows them to spin. The nacelle is located on the back of the blade and contains the generators. When the wind is strong enough, it will result in the blades spinning, which then activate the generators on the nacelle and generate electricity. The electricity then travels to a transformer, which transforms the energy into the appropriate voltage for the electrical grid. Below is a detailed look on the inside of a wind turbine.
Think of how a wind turbine works as the opposite of how a fan works. A fan uses electricity to make wind, while a wind turbine uses wind to make electricity. There are two types of wind turbines, horizontal-axis, and vertical-axis. Horizontal-axis wind turbines usually have two or three blades. The horizontal-axis wind turbines are placed with the blades facing into the wind. Vertical axis turbines are placed the same way and look similar to an eggbeater. Wind turbines can be placed in large farms on in bodies of water. Usually, multiple wind turbines are installed at once in the same area, which is called a wind farm. Wind farms are cost efficient and provide bulks of electricity to the electrical grids.
Sources: