I think everyone has such experience, when we were a kid we fall in crazy love of an idol. We listen to their songs over and over again. We buy their albums and even the cloth which idols spoke to. Some crazy idolaters waiting their idol shows up in the airport, the supermarkets, even on the streets. What’s more, a real crazy story is that a girl was so crazy about the idols and she did not want to study even if she was only 13 years old. The father crazy about an idol and her father endured a along time. One day she said, “ I love my idols more than my parents.” Her father was very angry when he heard this. He lost all conscious and killed his daughter then commit suicide. My classmate in my high school. She is crazy about a super star who is a handsome man. When she went shopping with me, she must went into the shop where the star advertised. She would buy a lot of stuff even if some objects that she would not use them. Some girls like idols so much they carve idols’ names on themselves’ arms. I think they are really crazy. So why some kids so crazy about celebrities and how could we keep idolaters emotion under control?
The definition of Idolater is that the person that admires intensely and often blindly one that is not usually a subject of worship. According to could you fall in love blindly, as a society, we put a lot of emphasis on appearances. Looks play a large part of our lives, whether it’s how we look or how we perceive others. Stars’ attractive faces or dance are powerful enough for a naive teenager. Kids go through physical and psychological transformations during that time and it is also time they need to put their passion on something. A real person may refuse their love, however, a celebrity won’t. In this case, they would volunteer their money and time for them. In this way, stars get suppot they want and spread more information about themselves through their fans. Secondly, teenagers lack of family love easily in love with stars. A lot of stars have tough childhood, they get over it and became famous. Teenagers with family issue will find the common between themselves and stars. Through this way, teenagers love them more and think of them as their mentor.
So I wondering if there is any physchological reason exists on the phenomenon? Evolutionary psychologist Francisco Gil-White, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia explians, “Humans have a biological predisposition towards recognising prestigious individuals and acting sycophantically towards them. In the ancestral environment, prestigious individuals would be followed by people who wanted to gain information about successful living. Modern-day children who follow celebrities may be more popular because they are using this inbuilt mechanism to determine who and what is ‘cool’ “. So actually admire celebrities kind of not our choice. We were born this way. Social evluation teach us to learn from the successful people. Especially when we are young and havn’t form judgment on the surroundings we are more easily get effected by others.
I think admire celebrities is not a hazard thing. However, we always need to keep in our mind that there is a line there. Like why we really obsess over celebrities says, “They are regular people in very high-profile jobs.” I once love a singer crazily, but after a few years the passion all gone. During the time I like him I didn’t spend a lot money on it, I just download his songs and listening. Sometimes talk to my friends how much I like him. I always keep in mind it’s not worth it to spend too much time and money on it. We are the master of ourselves’s life so don’t pay attention too much on celebrities life. Besides I think the right lead from teachers and families are really important. During the transformations time tell them such behavior is understandable but do not put too much passion on celebrities.
Finally, the idolaters can hurt themselves. On March, 20 2014, a new would be spread q
Sources:
http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/idolater
Could you fall in love blindly http://www.dearvagina.com/could-you-fall-in-love-blindly-literally/relationships/love-and-dating/
http://www.counselling-directory.org.uk/counsellor-articles/why-do-kids-actually-fall-in-love-with-celebrities



 A certain use of medicinal marijuana alleviated the intense and dangerous symptoms of Dravet Syndrome in a toddler by the name of Charlotte Figi. Dravet Syndrome is a rare form of epilepsy that causes frequent and sudden seizures that cannot be controlled by medication. This treatment “decreased [Charlotte’s] seizures from three hundred a week to just one every several days” (
A certain use of medicinal marijuana alleviated the intense and dangerous symptoms of Dravet Syndrome in a toddler by the name of Charlotte Figi. Dravet Syndrome is a rare form of epilepsy that causes frequent and sudden seizures that cannot be controlled by medication. This treatment “decreased [Charlotte’s] seizures from three hundred a week to just one every several days” ( Although as many as one in ten autistic individuals have Savant syndrome, only half of recorded savants are autistic. According to Dr. Darold Treffert, the syndrome is caused when there is either damage to or dysfunction in the left hemisphere of the brain and still-available brain tissue rewires in the right hemisphere and improves right hemisphere functions (
Although as many as one in ten autistic individuals have Savant syndrome, only half of recorded savants are autistic. According to Dr. Darold Treffert, the syndrome is caused when there is either damage to or dysfunction in the left hemisphere of the brain and still-available brain tissue rewires in the right hemisphere and improves right hemisphere functions (
 As I said before, it turns out that some stress is not harmful. Actually, short-term stress is showing signs of being very helpful to human’s immune health. Firdaus Dhabhar conducted a
As I said before, it turns out that some stress is not harmful. Actually, short-term stress is showing signs of being very helpful to human’s immune health. Firdaus Dhabhar conducted a  So what does this all mean? It means you may not want to listen to your relatives when they tell you all stress is bad. If you stress chronically, you may be at increased risks of becoming ill as Kiecolt-Glasser showed. However, if you stress a few hours before a big exam, or daunting lecture, you may just be increasing your odds of fighting off an attack to your immune system. The human body has a fight-or-flight response to stressful events for a reason. It is to help us. Not hurt us. It is not in your best interest to try to eliminate stress completely. Just keep it acute and not lasting months on end and you should not have to chalk your cold up to stress.
So what does this all mean? It means you may not want to listen to your relatives when they tell you all stress is bad. If you stress chronically, you may be at increased risks of becoming ill as Kiecolt-Glasser showed. However, if you stress a few hours before a big exam, or daunting lecture, you may just be increasing your odds of fighting off an attack to your immune system. The human body has a fight-or-flight response to stressful events for a reason. It is to help us. Not hurt us. It is not in your best interest to try to eliminate stress completely. Just keep it acute and not lasting months on end and you should not have to chalk your cold up to stress.





 e ghosts can show themselves in the form of dark shadows, and then try to prove that point. While that is one way to go about trying to prove something, it is not exactly the most scientific. Assuming theories about ghosts has not lead to any earth shattering breakthroughs. As we learned in class, the proper way to test a hypthosisies is by going through the scientific method. It is necessary to collect data and evidence, conduct tests, and use your results to draw a conclusion.
e ghosts can show themselves in the form of dark shadows, and then try to prove that point. While that is one way to go about trying to prove something, it is not exactly the most scientific. Assuming theories about ghosts has not lead to any earth shattering breakthroughs. As we learned in class, the proper way to test a hypthosisies is by going through the scientific method. It is necessary to collect data and evidence, conduct tests, and use your results to draw a conclusion.
 edically, it doesn’t make sense that that clinching your waist tightly will make it permanently smaller. Once you take the garment off, your body will return to its usual shape. It’s also uncomfortable, restricts your movements, and if you wear it really tight, it can even make it difficult to breathe and theoretically could cause rib damage.” This is a general consensus among experts. While it is thought that wearing the waister trainer makes you sweat more, the general rule is that 3,500 calories=1lb. With that being said, the amount you sweat from it will not cause your to lose so much weight you really see a difference.
edically, it doesn’t make sense that that clinching your waist tightly will make it permanently smaller. Once you take the garment off, your body will return to its usual shape. It’s also uncomfortable, restricts your movements, and if you wear it really tight, it can even make it difficult to breathe and theoretically could cause rib damage.” This is a general consensus among experts. While it is thought that wearing the waister trainer makes you sweat more, the general rule is that 3,500 calories=1lb. With that being said, the amount you sweat from it will not cause your to lose so much weight you really see a difference. help us lose weight quickly and keep it off, it just isn’t possible with changing your lifestyle. A well balanced diet with the right amount of complex carbs like bread, rice, and whole grain pasta, dairy/milk, lots of fruits and veggies, and protein are what is necessary to live a healthy life and see the results you want to see. Balance is essential in a healthy diet. It is important to eat the right amount of nutritious food in order to maintain a healthy body weight. The ideal plate is shown on the right, produced by Harvard’s Health Publications. In America, it is no secret that obesity is a problem. According to a national tally on
help us lose weight quickly and keep it off, it just isn’t possible with changing your lifestyle. A well balanced diet with the right amount of complex carbs like bread, rice, and whole grain pasta, dairy/milk, lots of fruits and veggies, and protein are what is necessary to live a healthy life and see the results you want to see. Balance is essential in a healthy diet. It is important to eat the right amount of nutritious food in order to maintain a healthy body weight. The ideal plate is shown on the right, produced by Harvard’s Health Publications. In America, it is no secret that obesity is a problem. According to a national tally on 
 nes across a couple of years. They found that there was a higher percentage of woman with blonde hair featured in the magazine than any other color. After reading these studies, it made me think more about this stereotype. It seems to me that people don’t take blonde haired woman seriously. People see them more as models or designers instead of CEOs or managers.
nes across a couple of years. They found that there was a higher percentage of woman with blonde hair featured in the magazine than any other color. After reading these studies, it made me think more about this stereotype. It seems to me that people don’t take blonde haired woman seriously. People see them more as models or designers instead of CEOs or managers.


 I don’t know about everyone else, but as it starts to get colder, I find myself becoming increasingly lazy and tired. The thought of going out on a Friday night is no longer as appealing as laying in my bed and binge watching a season of Grey’s Anatomy. Now obviously most people do not prefer to spend their time walking a few miles to their destination in the freezing cold, but I’m wondering, does the change in seasons actually effect your mood?
I don’t know about everyone else, but as it starts to get colder, I find myself becoming increasingly lazy and tired. The thought of going out on a Friday night is no longer as appealing as laying in my bed and binge watching a season of Grey’s Anatomy. Now obviously most people do not prefer to spend their time walking a few miles to their destination in the freezing cold, but I’m wondering, does the change in seasons actually effect your mood? 
 d an analogous decrease during autumn and winter months, that is a constant, if not a universal behavior that affects both the Norther and Southern hemisphere.” This was finding of a meta-analysis studying the link between seasons and suicide in 2012. In another study in Sweden, from 1992-2003 the same pattern was discovered. A peak for suicides was found in the spring and summer months.
d an analogous decrease during autumn and winter months, that is a constant, if not a universal behavior that affects both the Norther and Southern hemisphere.” This was finding of a meta-analysis studying the link between seasons and suicide in 2012. In another study in Sweden, from 1992-2003 the same pattern was discovered. A peak for suicides was found in the spring and summer months. Its that time of year again….the Victoria’s Secret Fashion Show. The moment girls wait for all year. The skinny, “perfect” models strut down the runway. It is nothing but glamorous. But for the women watching, how does this make them feel about themselves? Some love it and it makes them feel like models themselves. But some, on the other hand, go down a different route…
Its that time of year again….the Victoria’s Secret Fashion Show. The moment girls wait for all year. The skinny, “perfect” models strut down the runway. It is nothing but glamorous. But for the women watching, how does this make them feel about themselves? Some love it and it makes them feel like models themselves. But some, on the other hand, go down a different route… What does this have to do with the media? Well, the media is obsessed with what the best look is and will do anything to make money off an insecurity. It is almost impossible to go anywhere without seeing an airbrushed model on a magazine or the newest diet that could “make you drop forty pounds in ten days!!” There are unrealistic. If these diets were truthful, then one would have dominated the industry already. (ADA)
What does this have to do with the media? Well, the media is obsessed with what the best look is and will do anything to make money off an insecurity. It is almost impossible to go anywhere without seeing an airbrushed model on a magazine or the newest diet that could “make you drop forty pounds in ten days!!” There are unrealistic. If these diets were truthful, then one would have dominated the industry already. (ADA) entists believe that the media has nothing to do with the development of eating disorders, but how can that be true? With the desire to be thin in every direction and now at almost every age, it is almost like if you aren’t thin, you are an outcast. From shows like “The Biggest Loser”, anyone who watches them can be influenced. Even children can watch these shows and question their body.
entists believe that the media has nothing to do with the development of eating disorders, but how can that be true? With the desire to be thin in every direction and now at almost every age, it is almost like if you aren’t thin, you are an outcast. From shows like “The Biggest Loser”, anyone who watches them can be influenced. Even children can watch these shows and question their body.

 What exactly is a black hole?
What exactly is a black hole? 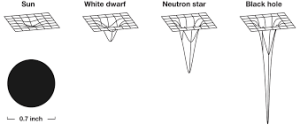 up to 20 times greater than the mass of the sun and can fit inside a ball with a diameter of about 10 miles. Dozens of stellar mass black holes may exist within the
up to 20 times greater than the mass of the sun and can fit inside a ball with a diameter of about 10 miles. Dozens of stellar mass black holes may exist within the  surrounding it. A star’s motion is the key factor in determining if a black hole is around it. Generally, if it is orbiting a point in space, there is a black hole there. High-energy light is produced by stars and black holes being close. Scientists can use specific instruments to see this light, which is another way to find black holes. There is something called a accretion disc, which is defined as “a black hole’s gravity that is strong enough to pull off the outer gases of the star and grow a disk around itself,” according to Nasa. This disk releases X-ray lights due to it’s high temperatures, which makes it possible for scientist’s telescopes to pick up on the light. This is one of the many methods scientists use to pick up on black holes.
surrounding it. A star’s motion is the key factor in determining if a black hole is around it. Generally, if it is orbiting a point in space, there is a black hole there. High-energy light is produced by stars and black holes being close. Scientists can use specific instruments to see this light, which is another way to find black holes. There is something called a accretion disc, which is defined as “a black hole’s gravity that is strong enough to pull off the outer gases of the star and grow a disk around itself,” according to Nasa. This disk releases X-ray lights due to it’s high temperatures, which makes it possible for scientist’s telescopes to pick up on the light. This is one of the many methods scientists use to pick up on black holes.










 Have you ever felt your melting brain dribble out of your ears after watching a few hours of TV? Didn’t think so. If you said yes, definitely get off your computer and go see a doctor. For the rest of you without liquified brains. I’m sure you’ve heard about some of the negative aspects of watching TV. I know, the Big Bang Theory is super funny but you should really go outside. Humans are not meant to spend most of their time sedentary, that means you! It has long been known that the advent of television has contributed to obesity related diseases. But does it make you dumb? There is some evidence out there that suggests just that! Before you call your mom and tell her that your bad mid term grade was Modern Family’s fault, lets check it out.
Have you ever felt your melting brain dribble out of your ears after watching a few hours of TV? Didn’t think so. If you said yes, definitely get off your computer and go see a doctor. For the rest of you without liquified brains. I’m sure you’ve heard about some of the negative aspects of watching TV. I know, the Big Bang Theory is super funny but you should really go outside. Humans are not meant to spend most of their time sedentary, that means you! It has long been known that the advent of television has contributed to obesity related diseases. But does it make you dumb? There is some evidence out there that suggests just that! Before you call your mom and tell her that your bad mid term grade was Modern Family’s fault, lets check it out.


