Mostly every college student has done it. You’re about to go on a long drive, you just stopped to get some gas and you grab a red bull to keep you awake and alert. But did you know that drinking that Red Bull could of been highly beneficial for your driving ( I honestly didn’t)?Of course energy drinks are not the greatest thing for your health but scientific studies do indeed show results of Red Bull having a positive effect on the body when driving for a long duration of time.

https://www.google.com/search?q=road+trip&rlz=1C1CHBD_enUS710US710&espv=2&biw=1597&bih=870&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiIuISIt-rPAhXm34MKHX58D8UQ_AUIBigB&dpr=0.75#imgrc=LKUv-Yis7qhkWM%3
Personally when I think of red bull, I think action sports, adrenaline, and wings. But after I read this study that consisted of a somewhat small sample but provided some interesting results. The scientific study consisted of a double-blind placebo experiment with 24 healthy individuals. The results were basted off an experiment that simulated driving four hours. Half the drivers were given Red Bull and the others were given Red Bull without most of the ingredients as in caffeine, B vitamins, etc.. Each individual would would drive for a short period, receive the Red Bull or the placebo drink then drive for four straight hours.
The results of the experiment were quiet interesting. You would think for over a long period of time the drink would make you groggy, but in fact, drinking the Red Bull brought positive effects to the individuals that received it. The results indicate that the study shows drinking Red Bull while driving long distances improved the quality of the driving of the individuals that drank it, there was a reduction of speed and finally, it provided the drivers metal benefits that helped preform the task of driving more efficiently. So the overall conclusion of the study was that drastically improves the performance of the driver as well as reduces the feeling of be tired during long driving periods.
So there is a few flaws that I would like to address and discuss. The first flaw is that the experiment was only done on 24 individuals which indicates a fairly small sample size. The second flaw is that they took out over six ingredients for the placebo group of the study. My question is what if just one of those ingredients was the overall factor of receiving positive effects. The study cannot provide and answer as to what is the main ingredients that do provide the positive benefits and if there is a way to indicate those specific ingredients, can we create a healthier alternative that provides the same effects?
Overall, I believe that drinking Red Bull does indeed bring positive effects on driving. Do you think it is? Do you think their is a healthier alternative beside Red Bull that will provide the same effects or is Red Bull the overall drink to consume when driving long distances?







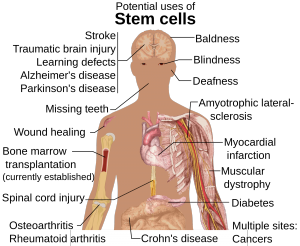














 ascinating in the sense that the experimental group performed significantly better than the control group when tested on their retention of vocabulary words. Not only did the experimental group of English students retain vocabulary words better when music was involved, but this group also had a better outlook on their English course, and an overall higher performance rate in the English class.
ascinating in the sense that the experimental group performed significantly better than the control group when tested on their retention of vocabulary words. Not only did the experimental group of English students retain vocabulary words better when music was involved, but this group also had a better outlook on their English course, and an overall higher performance rate in the English class.







 explains how they are made. As seen in the video using GMOs can benefit a plant when fighting disease. This is nothing new, farmers have done cross breading for many years in order to have a plant that is more resistant to disease. The only problem with the method of cross breading is that it can take many years, however, with GMOs it takes substantially less time with better results. As seen in the video when treating a plant for a disease it works that same way as getting a flu shot. The plants genes are modified, often times giving it a gene from the disease, in order for it to build up a resistance.
explains how they are made. As seen in the video using GMOs can benefit a plant when fighting disease. This is nothing new, farmers have done cross breading for many years in order to have a plant that is more resistant to disease. The only problem with the method of cross breading is that it can take many years, however, with GMOs it takes substantially less time with better results. As seen in the video when treating a plant for a disease it works that same way as getting a flu shot. The plants genes are modified, often times giving it a gene from the disease, in order for it to build up a resistance. one part it can have a bigger effect than people think. Another common argument against GMOs is that it causes allergies. According to
one part it can have a bigger effect than people think. Another common argument against GMOs is that it causes allergies. According to 
















