We all know the say… “Boys go to Jupiter to get more stupid-er”. Only kidding. However, this topic did spark an interest in me: how do the brains of women and men differ? Do we remember things differently? Are women more inclined with their short term memory than men? Is THAT why you guys are always forgetting things we tell you, or do you just not listen? Honestly, it might be a little bit of both. Nonetheless, I decided to investigate the male and female brains further.

House of Hoxshore
The study
The first study I looked into was focused on evaluating the correlation between multitasking and short term memory in male and female college students. This study merely evaluated 6 subjects: 3 men and 3 women in college. Prior to tests, the subjects underwent a pre-questionnaire. Following the questionnaire, the subjects entered a virtual spherical room with pictures designed specifically for the study. They allotted approximately 60 seconds for each subject, recording the tour, as well as pinpointing specific pictures the subjects focused in on. After the tour, the subject underwent a post questionnaire, asking them specific questions regarding the tour. For example, the subjects had to identify which wall they saw specific photos on. The goal of this experiment was to analyze male and female recollection, how it compares and how it differs, and ultimately to support or refute the hypothesis.
Hypothesis: Female subjects would test better on the post tour questionnaire, indicating their short term memory is stronger than male subjects.
The results
After the study, the authors concluded that females scores were drastically better than males. This means that during the post tour questionnaire, the females were successfully able to indicate the photos in relation to the virtual room. Out of 12 photos in various locations, the male subjects tended to accurately place 2-4 of the pictures in the room. While the females recalled 5-9 successfully. Based off of the numbers, the authors supported their hypothesis: female subjects tested higher than male subjects. This could potentially lead to the assumption that females possess stronger short term memory traits than males. Though the results of the study supported the hypothesis, a study with merely 6 subjects is often hard to view as accurate when speaking of percentages. In this study specifically, the females tested 40% higher than the males. A study with a larger subject group may decrease the percentage gap.
Pinterest
How men and women differ
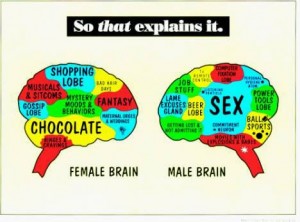
It’s simple: men and women are wired differently, point blank. Ragini Verma, a radiologist at the University of Pennsylvania, conducted a study in which they tested the brains of 400 male subjects and 500 female (ages 8-22). By scanning the brains, they found some pretty notable results: female brains tended to be most connected between left and right hemispheres, triggering the social and emotional tendencies of women we are all used to. On the other hand, the male brain connections focused more so in the back of the brain, which is the action and perception – also known as the manly man tendencies.
To break it down further, I came across a Masters of Healthcare blog titled “10 Big Differences Between Men’s and Women’s Brains”. Up until this point, most articles shared on the brain differences were filled with complex wording and terms I couldn’t even pronounce. So luckily, Amber Hensley broke it down in a way I could understand. Here were a couple of her points:
- Human interactions: this correlates with Verma’s findings between hemispheres. Women tend to thrive more with interaction – emotion, empathy, comfort. They are also more intuitive with body language, and nonverbal relationships. This means that women are better suited for nonverbal communication and comforting, whereas men tell it like it is. Black or white, and expect people to all do the same. I mean, how many times are women secretly upset at men, but will deny being mad, and so the man accepts that she’s not mad and moves on; except, the woman is upset, and he’s about to have an earful. Women are in touch with their emotions and feelings (most of the time), whereas men want to see a problem, and physically fix it.
- Stress reactions: in a previous blog of mine I evaluated the term “fight or flight”, which is essentially a chemical reaction in your body that tells you to fight, or to flee. Men generally possess the “fight or flight” reaction. Women, on the other hand, “tend and befriend” (term credited to psychologist, Shelley E. Taylor). In stressful situations, women are wired to nurture, to comfort, and to congregate in groups.
- Pain: this one is super interesting – men and women are even wired to handle pain differently. Women often require more morphine than men to reduce pain, this is found to be because women perceive pain much more intensely than men. On top of that, though not very surprising, men are less likely to vocalize their pain, which explains how they can get sacked so hard playing football, and just walk it off without a tear. Me? I cry when I get a shot. According to Hensley, the amygdala is the portion of the brain in which interprets pain. When men experience pain, the right side (connected with external uses) is active, whereas women activate their left side (connected with internal uses). Weird, huh?
Conclusion
All in all, men and women are drastically different in regards to the brain. Women may have better short term memory, but that does not make them the winners here (sorry, ladies). It’s sort of funny how it’s a balancing act – what women lack, men possess, and vice versa. The various studies shed light on several concepts highlighting the differences, making it easier to understand. So ladies, next time you’re mad at a male for not understand why you’re upset, don’t blame him, his brain was not physically wired that way, be patient and he will figure it out eventually. And men, when a woman tells you “nothing is wrong”, you better believe something is wrong. Go buy some flowers.
Sources
“Short Term Memory Based on Gender – Clemson University.” N.p., n.d. Web. 21 Oct. 2016.
Grant, Bob. “Male and Female Brains Wired Differently | The Scientist …” The Scientist. N.p., 4 Dec. 2013. Web. 21 Oct. 2016.
Hensley, Amber. “10 Big Differences Between Men’s and Women’s Brains …” Masters of Healthcare. N.p., 16 June 2009. Web. 21 Oct. 2016.
















 Looking at this from a scientific perspective, to determine wether the hypothesis is true that stress is to blame for poor health, we need to consider other possible causations. What if people that have poor health are more likely to become stressed, this would cause a potential flaw in the results (reverse causation). Overall, people put in stressful situations should look for some type of treatment since there will be no good outcome.
Looking at this from a scientific perspective, to determine wether the hypothesis is true that stress is to blame for poor health, we need to consider other possible causations. What if people that have poor health are more likely to become stressed, this would cause a potential flaw in the results (reverse causation). Overall, people put in stressful situations should look for some type of treatment since there will be no good outcome.


 is where the brain begins to have very slow activity and the person is difficult to wake up. Finally stage five is where the brain reaches REM, this is where people begin to have dreams and are the most difficult to wake up. After learning the process of sleep, it is important to know why it is crucial to living a healthy life.
is where the brain begins to have very slow activity and the person is difficult to wake up. Finally stage five is where the brain reaches REM, this is where people begin to have dreams and are the most difficult to wake up. After learning the process of sleep, it is important to know why it is crucial to living a healthy life.

 not clinically prescribe someone to the medication, they are putting their health at potential risk. Clearly this shows that the majority of students use them for school related reasons, because they think it “helps” them focus on school work. However, increased focus obtained by these drugs does not actually enhance intelligence in any way, it may only help the duration of focus on a task. For example, if a student wanted to study late through the night, stimulants will help him or her stay awake and alert, but it is unhealthy for the body to be forced to stay awake in times of rest.
not clinically prescribe someone to the medication, they are putting their health at potential risk. Clearly this shows that the majority of students use them for school related reasons, because they think it “helps” them focus on school work. However, increased focus obtained by these drugs does not actually enhance intelligence in any way, it may only help the duration of focus on a task. For example, if a student wanted to study late through the night, stimulants will help him or her stay awake and alert, but it is unhealthy for the body to be forced to stay awake in times of rest.